brain

Expand All | Collapse All
Normal
- architecture
- cerebrum
- cerebellum
- pons
- medulla
- ventricle
- choroid plexus
- thalamus
- hypothalamus
- pituitary
- pineal
- components
- gray matter: rich in cell bodies of nerves and glia
- white matter: rich in axons forming tracts and fascicles
- neuropil: rich in unmyelinated axons forming networks of synapses
- meninges: dura (dense collagen, calcifications), arachnoid (mesothelial lining), pia (mesothelial lining, loose connective tissue)
- CNS lacks connective tissue and lymphoid elements
- cell types
- neuron
- glial = the non-neural cells
- astrocyte
- oligodendrocyte
- ependymal cell
- microglia
WHO neoplasms
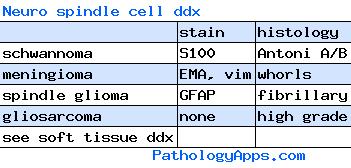
- Meningeal
- meningioma
- mesenchymal non-meningothelial tumors
- hemangiopericytoma
- melanotic lesions
- hemangioblastoma
- Sellar (see pituitary)
- craniopharyngioma
- granular cell tumor
- pituicytoma
- spindle cell oncocytoma
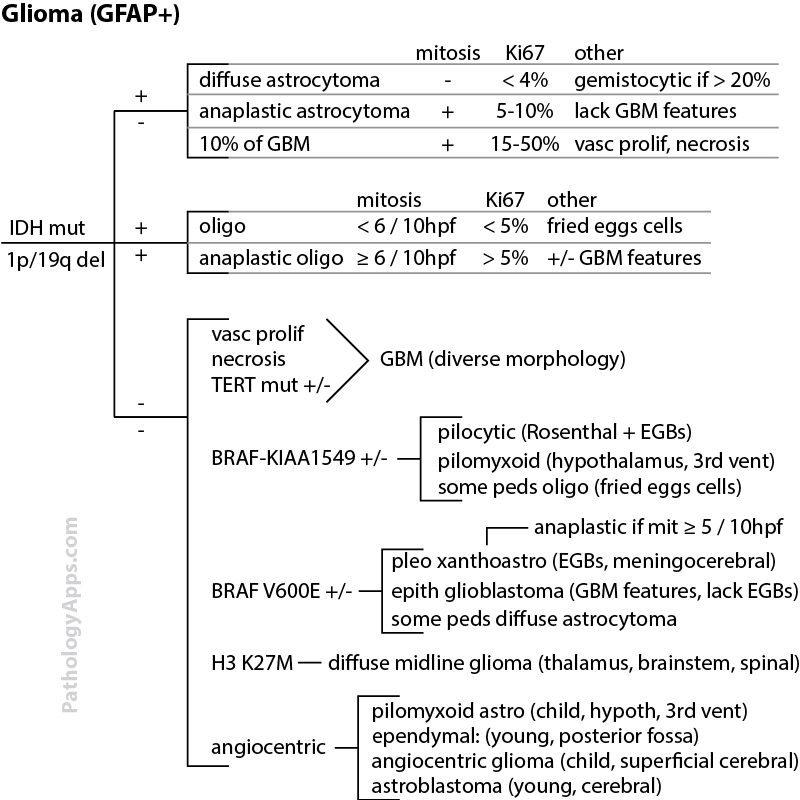
- Astrocytic
- pilocytic astrocytoma
- pilomyxoid astrocytoma
- pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- diffuse astrocytoma
- anaplastic astrocytoma
- glioblastoma
- giant cell glioblastoma
- gliosarcoma
- gliomatosis cerebri
- SEGA
- Oligodendroglial
- Ependymal
- Choroid plexus
- Other neuroepithelial
- astroblastoma
- chordoid glioma of the third ventricle
- angiocentric glioma
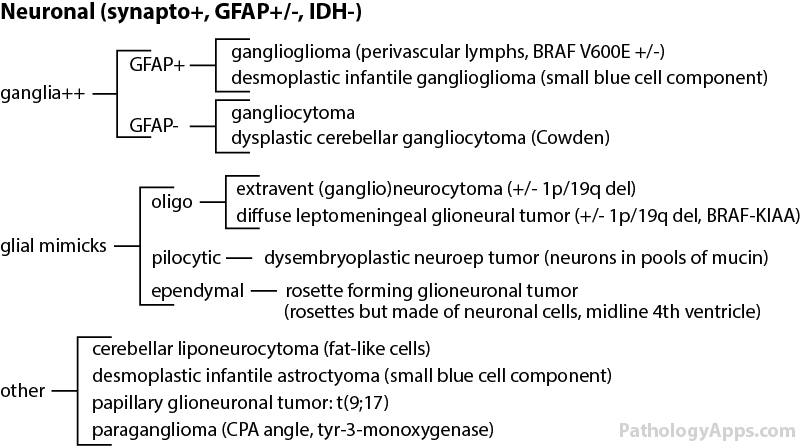
- Neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial
- desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma and ganglioglioma
- dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
- ganglioglioma
- gangliocytoma
- central neurocytoma and extraventricular neurocytoma
- cerebellar liponeurocytoma
- papillary glioneuronal tumor
- rosette-forming glioneuronal tumor of the fourth ventricle
- paraganglioma (spinal)
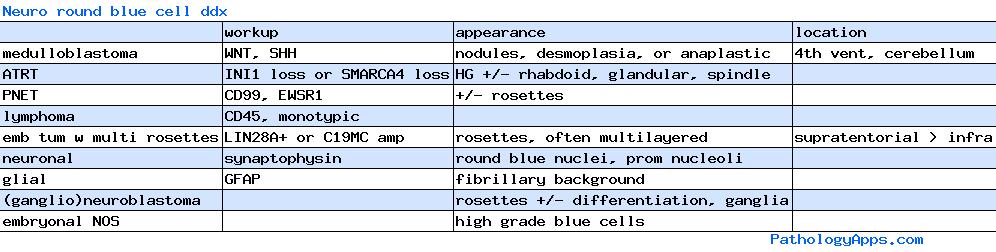
- Embryonal
- medulloblastoma
- PNET
- medulloepithelioma
- ependymoblastoma
- ATRT
- Cranial and paraspinal nerves
- schwannoma
- neurofibroma
- perineurioma
- MPNST
- Hematopoietic
- lymphoma
- histiocytic tumors
- GCTs
- Metastasis
Ddx by location
- Cerebral ddx
- peds
- adult
- oligodendroglioma
- diffuse glioma
- GBM
- metastasis
- lymphoma
- Hypothalamus ddx
- Thalamus ddx
- Cerebellar ddx
- Brainstem ddx
- pilocytic astrocytoma
- brain stem glioma
- gliomatosis cerebri
- CPA ddx
- schwannoma
- meningioma
- choroid plexus tumor
- Ventricular ddx
- lateral ventricle
- 3rd ventricle
- 4th ventricle
- periventricular
- Pituitary ddx
- Pineal ddx
- pineocytoma
- pineal cyst
- germinoma
- pineoblastoma
Inflammation ddx
- meningitis
- encephalitis
- HSV
- EBV
- CMV
- PML
- rabies
- HIV leukoencephalopathy
- neurocysticercosis
- west nile encephalitis
- RMSF
- other
- parasites
- CNS malaria
- amebic encephalitis
- trypanosomiasis
- lymphocytic choriomeningitis
- California encephalitis
- subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
- progressive rubella encephalitis
- parasites
- abscess
- other
- neurosarcoidosis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- Wegener disease
Vascular ddx
- stroke
- ischemic
- hemorrhagic
- lacunar infarct
- hypertensive encephalopathy
- amyloid angiopathy
- vasculitis
- giant cell arteritis
- primary angiitis
- polyarteritis nodosa
- aneurysm
- vascular malformations
- AVM
- cavernous hemangioma
- capillary telangiectasia
- venous angioma
- other
- CADASIL
- Moyamoya syndrome
Degenerative ddx
- Alzheimer disease
- Parkinson disease
- Lewy body dementia
- progressive supranuclear palsy
- corticobasal degeneration
- multiple system atrophy
- frontotemporal lobar degeneration
- prion disease
- CJD
- kuru
Syndromes
- NF1
- NF2
- vHL
- Tuberous sclerosis
- Li-Fraumeni
- Cowden
- Turcot
- Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- Rhabdoid tumor predisposition syndrome
