glioblastoma

Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- most common brain tumor
- mean age 60
- site: hemispheres, subcortical white matter
- mostly de novo, can arise from diffuse and anaplastic astrocytoma
- WHO grade IV
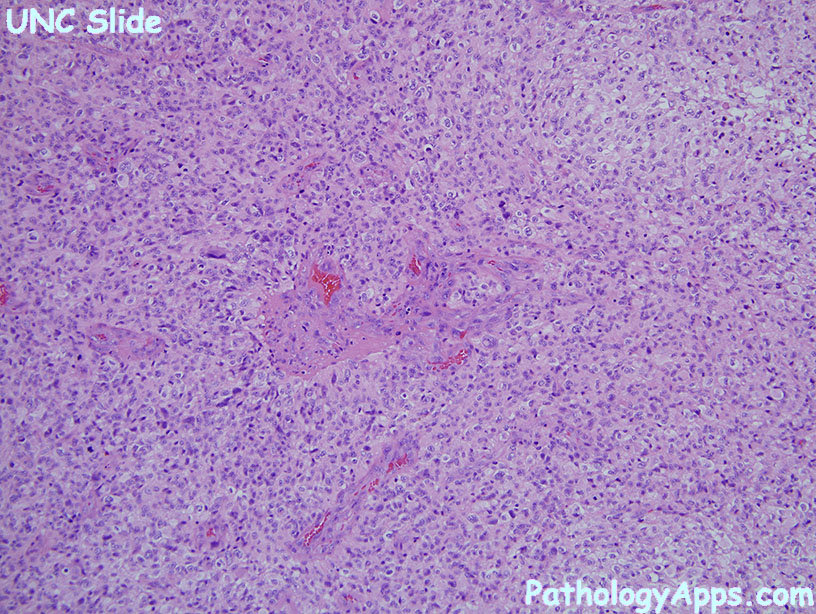
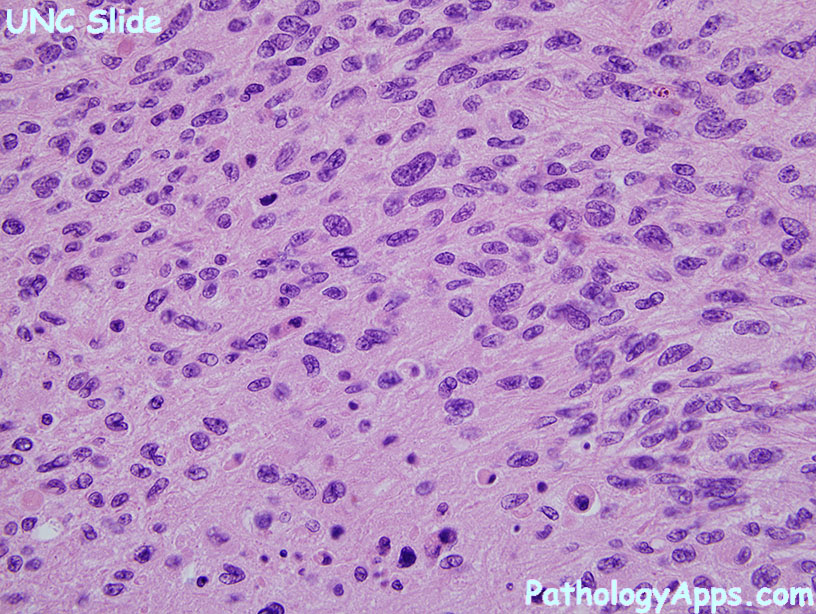
Histology
- anaplastic glial cells
- abundant mitosis
- necrosis (pseudopalisading) or microvascular proliferation
- other possible components
- metaplasia: adenoid (glandular), squamous
- oligodendroglial component
- gemistocytes, granular cells, lipidized cells
- variants
- giant cell glioblastoma
- giant cells are S100+ and GFAP variable
- gliosarcoma
- biphasic (separate or mixed) glioblastoma and sarcoma component
- sarcoma component loses GFAP
- giant cell glioblastoma
Ddx
- demyelinating disease (lots of macrophages)
- lymphoma (perivascular cuffing)
- abscess
Molecular
- get IDH1/2, 1p19q, MGMT for therapy purposes
