stomach
Expand All | Collapse All
Normal
- portions
- cardia: mucinous glands
- fundus: oxyntic mucosa
- body: oxyntic mucosa
- antrum: mucinous glands
- pylorus: mucinous glands
- greater curvature: attaches to omentum and transverse colon mesentery
- lesser curvature: attaches to liver by gastrohepatic ligament
- layers
- mucosa
- foveolar pits
- shorter in body (1/4 thickness)
- longer in cardia and antrum (1/2 thickness)
- tall columnar mucinous lining
- basal nuclei
- same epithelium throughout stomach
- neck: base of foveola, contains mucous neck cells, slightly larger nuclei than foveola
- deep glands: oxyntic glands in body and fundus, mucinous glands elsewhere
- lamina propria: scattered mononuclear cells are normal. Too much is chronic gastritis.
- muscularis mucosa
- foveolar pits
- submucosa
- can have fat
- muscularis propria
- inner oblique
- middle circular
- Auerbach plexus
- outer longitudinal
- subserosa
- serosa
- mucosa
- gland types
- oxyntic glands
- contains parietal and chief cells
- mucinous glands
- bubbly mucinous cytoplasm
- basal nuclei
- oxyntic glands
- cell types
- parietal cell
- pink, central nuclei
- makes acid and intrinsic factor
- more prominent in upper mucosa
- chief cell
- makes enzymes
- blue, basal nuclei, cuboidal-columnar
- more prominent in deeper mucosa
- endocrine cells
- gastrin G cells in antrum
- histamine ECL cells in body
- parietal cell
- Signout
- Benign gastric mucosa
- No dysplasia, intestinal metaplasia, or gastritis identified
- No H. Pylori identified on H&E
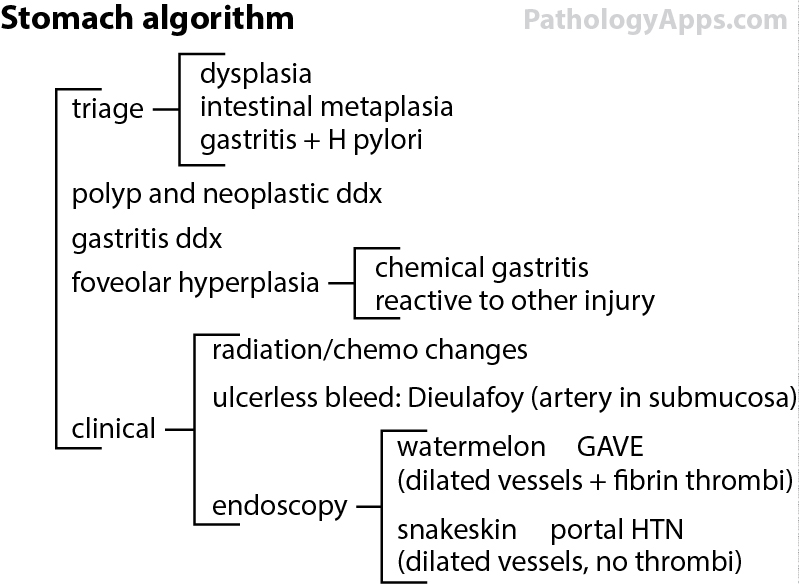
Approach
- epithelial abnormalities
- dysplasia: HG present? vs reactive
- carcinoma
- intestinal metaplasia
- foveolar hyperplasia
- PPI effect
- stromal infiltrate
- soft tissue tumor
- hematolymphoid
- gastritis
- clinical cues
- H. Pylori, gastritis
- polyps: fundic gland polyp, hyperplastic polyp, others
- watermelon stomach/strips on endoscopy: GAVE
polyp
gastritis
neoplasm
Other
- foveolar hyperplasia
- PPI effect
- reactive gastropathy
- therapy induced gastropathy
- gastric antral vascular ectasia
- portal hypertensive gastropathy
- peptic ulcer
- Dieulafoy lesion
- Kayexalate crystals
- bariatric surgery
- amyloidosis
- xanthoma
- pseudo-signet ring cells
- gastric mucosal calcinosis
Metaplasia
- intestinal metaplasia
- pyloric metaplasia
- paneth cell metaplasia
- pancreatic metaplasia
- pancreatic heterotopia
TNM (useful for grossing)
- Carcinoma
- Tis: in situ
- T1a: lamina propria or muscularis mucosa invasion
- T1b: submucosa invasion
- T2: muscularis propria invasion
- T3: subserosa invasion
- T4a: serosa perforation
- T4b: adjacent structure invasion
- N1: 1-2 regional nodes
- N2: 3-6 regional nodes
- N3a: 7-15 regional nodes
- N3b: 16+ regional nodes
- Carcinoid
- Tis: in situ, < 0.5 mm, mucosa confined
- T1: 0.5 mm to 1 cm, submucosa confined
- T2: > 1 cm or muscularis propria invasion
- T3: subserosa invasion
- T4: serosa perforation or adjacent structure invasion
- GIST
- T1: <= 2 cm
- T2: > 2 cm and <= 5 cm
- T3: > 5 cm and <= 10 cm
- T4: > 10 cm
- Grading
- low mitotic rate: <= 5 mitosis per 50 hpf
- high mitotic rate: > 5 mitosis per 50 hpf
Staging
- Carcinoma
- 0: Tis
- IA: T1
- IB: T2 or T1 N1
- IIA: T3, T2 N1 or T1 N2
- IIB: T4a, T3 N1, T2 N2, or T1 N3
- IIIA: T4a N1, T3 N2, or T2 N3
- IIIB: T4b N0-1, T4a N2, or T3 N3
- IIIC: T4b N2-3 or T4a N3
- IV: M1
- Carcinoid
- 0: Tis
- I: T1
- IIA: T2
- IIB: T3
- IIIA: T4
- IIIB: N1
- IV: M1
- GIST (gastric and omental)
- IA: T1-2
- IB: T3
- II: T4 or T1-2 and high mitosis
- IIIA: T3 and high mitosis
- IIIB: T4 and high mitosis
- IV: N1 or M1
