HSIL




Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- 0.5% of all paps
- 97% HPV+
- 60% will have CIN2
- 2% will have SCC
- management
- LEEP
- or colposcopy with endocervical assessment
Criteria
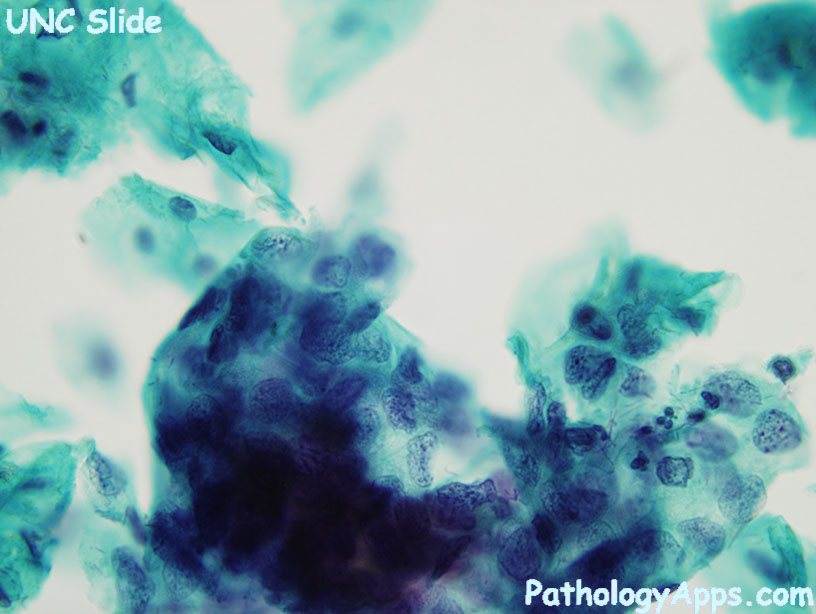
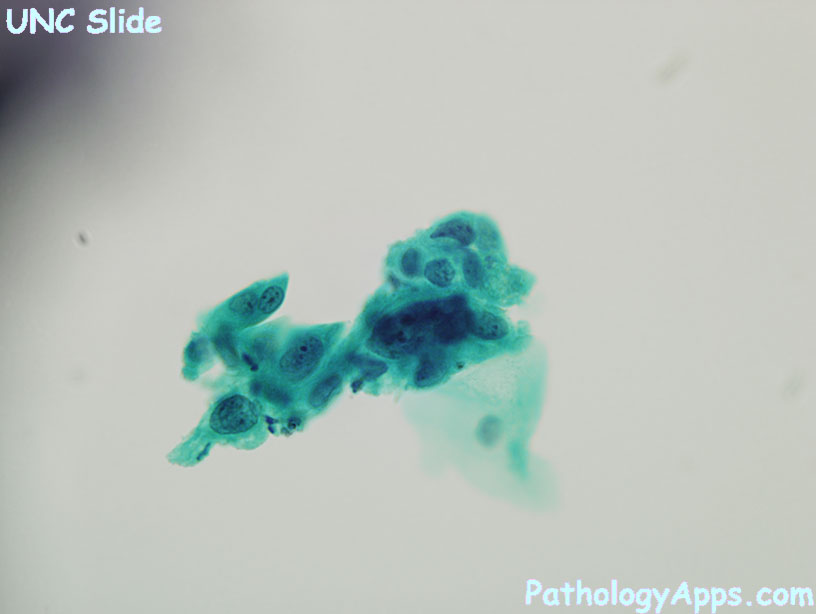
- cell smaller, less mature than LSIL
- singly, sheets, or syncytial aggregates
- NC ratio markedly increased
- irregular nuclear membrane
- nucleoli inconspicuous
- variable other nuclear atypia
- hyerchromasia
- irregular chromatin
- cytoplasm ranges from immature to keratinized
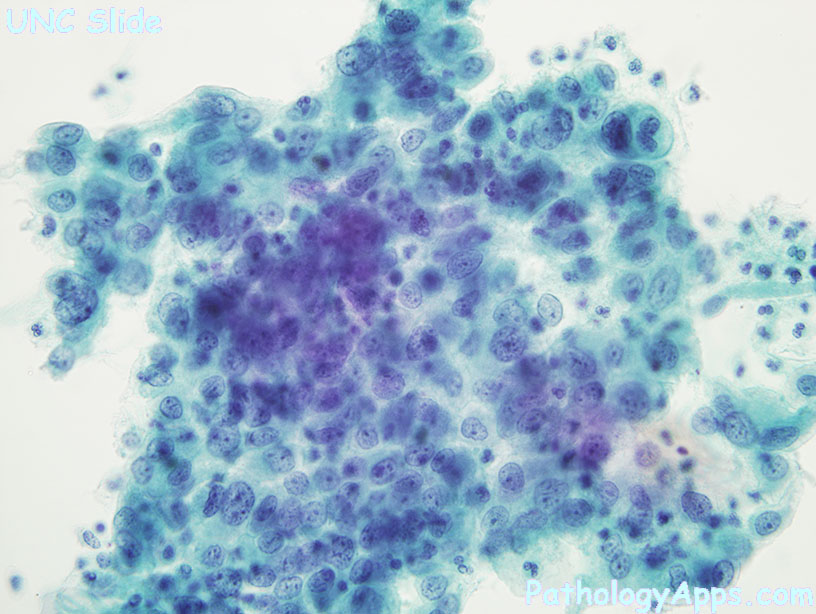
Patterns
- atypical cells with high NC ratio
- syncytial aggregates
- hyperchromatic crowded group
- nuclear atypia
- high NC ratio
- size variation
- hyperchromasia
- coarse chromatin
- irregular nuclear membrane
- HSIL involving endocervical gland
- central nucleus
- nuclear atypia
- endocervical cells on periphery
- abnormal stripped nuclei
- HSIL streaming in mucus
- HSIL in atrophy
- keratinzing HSIL
Ddx
- reserve cells
- parabasal cells
- ASCH
- SCC
- HSIL plus
- prominent nucleoli
- necrotic debris
- atrophy
- postmenopausal
- fine chromatin
- ASCUS with atrophy
- squamous metaplasia
- transitional metaplasia
- older women
- irregular nuclear contours
- nuclear grooves
- but minimal hyperchromasia
- abundance of coffee bean nuclei
- glandular
- endometrial cells
- smaller than HSIL
- spherical
- well circumscribed
- AIS
- endometrial cells
- reactive
- IUD
- prominent nucleoli
- histiocytes
- fine chromatin
- follicular cervicitis
- IUD
- endocervical polyp atypia
- pregnancy
- decidua
