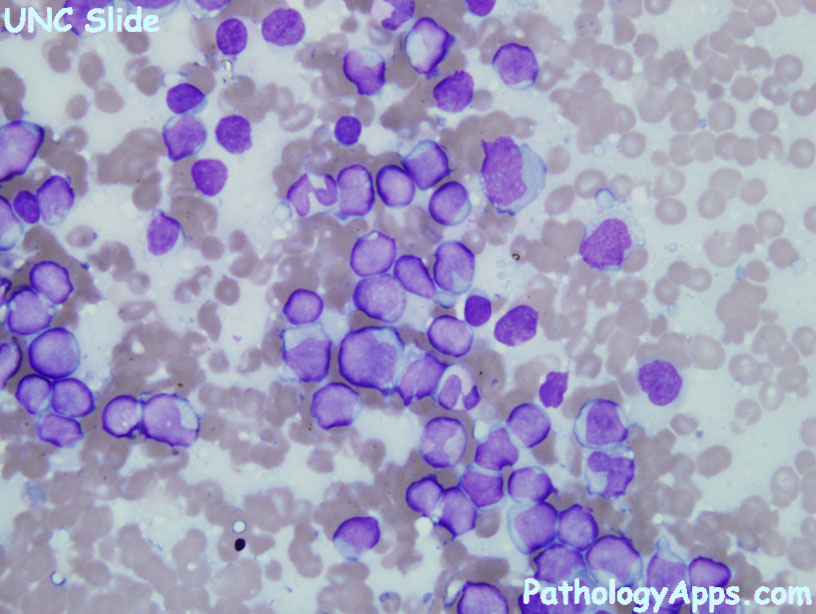
AML
Expand All | Collapse All
Diagnostic
- favorable prognosis
- t(8;21) RUNX1
- inv16
- NPM1
- CEBPA
- worse prognosis
- c-KIT with t(8;21) and inv(16)
- t(6;9)
- FLT3
- MDS cytogenetics
- diagnostic regardless of blast count
- t(8;21)(q22;q22); RUNX1-RUNX1T1
- inv16
- APML
- morphology
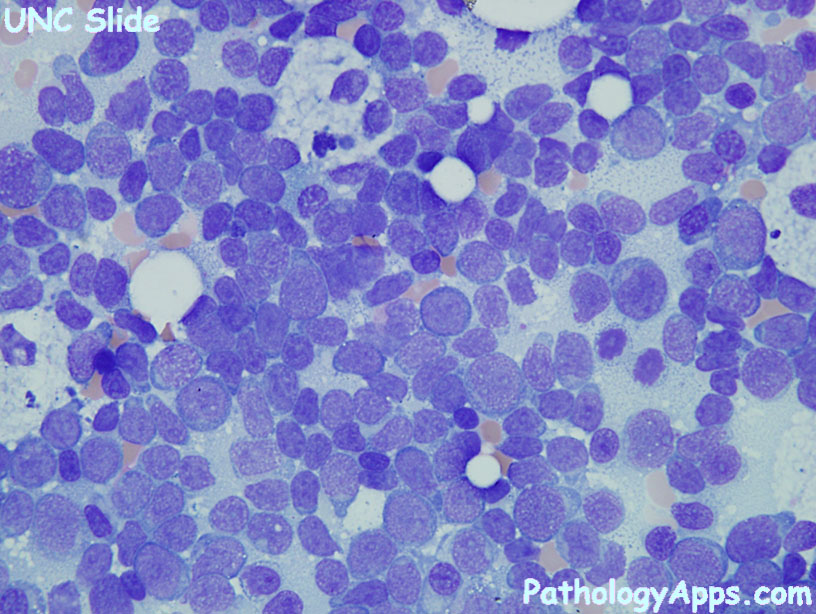
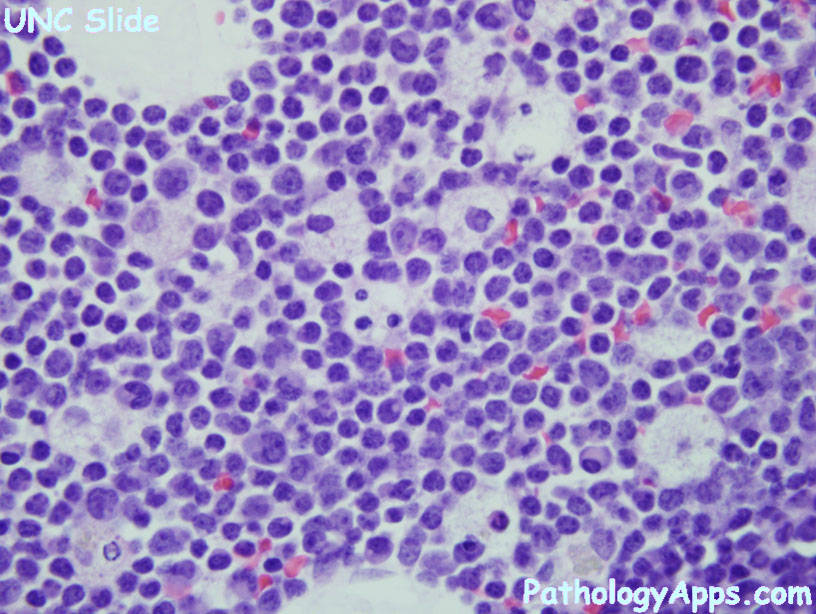
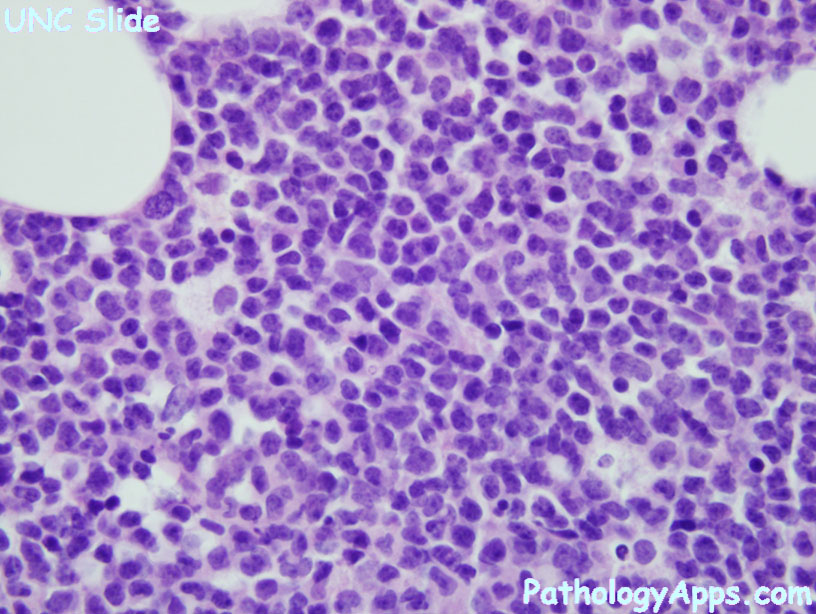
- blasts > 20%
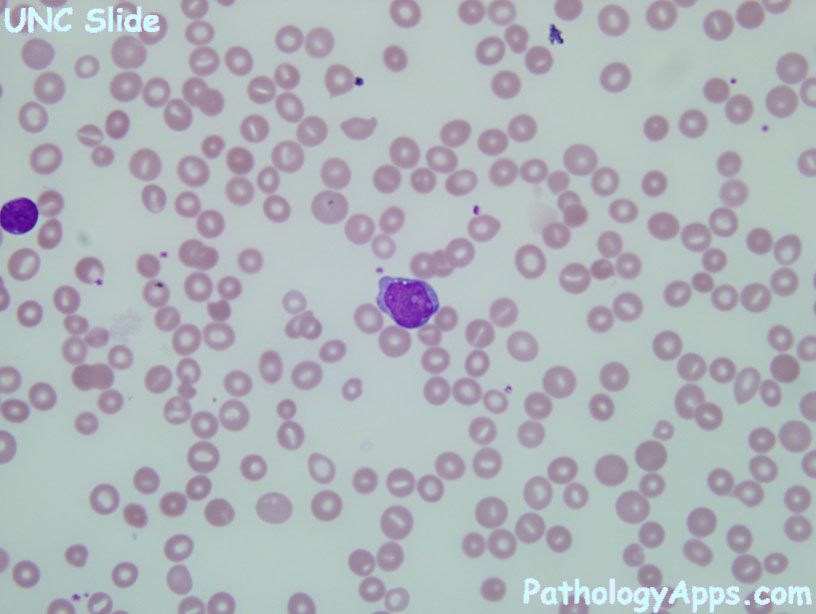
- Auer rods
Therapy & monitoring
- During therapy
- lack of blast reduction at day 6 of induction results in change or augmentation
- residual blasts at the end of induction = poor prognosis
- APML response to therapy can be maturation of promyelocytes rather than marrow ablation
- Residual disease
- blast >= 5%, compare with prior morphology
- blasts without maturation, and increases on repeat biopsy
- stains: CD34+ clusters
- flow: aberrant (CD2, 5, 7), asynchronous, and overexpression (CD33, 34)
- molecular, chimerism
- Remission criteria
- neutrophil > 1E9
- platelet >= 100
- blast < 5% without Auer rod
- Shortened remission if hypercellularity, anemia, or borderline blast count(1% marrow, 3% blood)
Recurrent abnormalities
- RUNX1
- t(8;21); RUNX1-RUNXT1
- large blasts with hof, can have large pink granules
- neutrophil lineage
- positive: CD34, HLADR, MPO, CD13
- weak: CD33
- inv16
- eosinophils with purple granules and aberrant CAE+
- monocytic and granulocytic differentiation
- CD34, CD117
- APML
- t(15;17); PML-RARA
- clinical: DIC, treat with ATRA
- promyelocytes with dense Auer rods
- types: hypergranular, microgranular (paucity of granules, bilobed nuclei, marked leukocytosis)
- positive: CD33
- heterogeneous: CD13
- low/negative: HLADR, CD34, CD11a
- MLL
- t(9;11); MLLT3-MLL
- can have DIC
- monocytic (monoblasts, promonocytes)
- positive: CD33, CD65, CD4, HLADRNSE
- weak: CD34, CD13, CD14
- negative: MPO
- DEK-NUP
- t(6;9); DEK-NUP214
- anemia, thrombocytopenia
- basophilia (>2%), multilineage dysplasia
- inv3
- can arise from prior MDS
- giant platelets
- monolobated/bilobated megakaryocytes, multilineage dysplasia
- positive: CD34, HLADR, CD13, CD33, CD38
- megakaryoblastic
- t(1;22); RBM15-MKL1
- megakaryoblasts
- rare, infants and age < 3, organomegaly
- positive: CD41, CD61
- negative: CD34, CD45, HLADR, MPO, SBB
- NPM1
- myelomonocytic or monocytic features
- female predominance, lack MDS or MPN history
- positive: myeloid (CD13, CD33, MPO), monocytic (CD14, CD11b), CD68, NPM (cytoplasmic), C23 (nuclear)
- negative: CD34
- CEBPA
- positive: CD34, HLADR, myeloid (CD13, CD33)
- negative: monocytic (CD14, CD64)
AML with MDS
therapy related myeloid neoplasm
AML NOS
- AML with minimal differentiation
- positive: CD34, CD38, HLADR
- negative differentiation markers: MPO, SBB, CAE, Auer rods
- negative maturation markers: CD11b, CD15, CD14, CD64, CD65
- AML without maturation
- positive differentiation: myeloid (CD13, CD33, CD117), at least 3% MPO or SBB, has Auer rods
- positive: CD34, HLADR
- negative maturation markers: CD15, CD65, CD14, CD64
- AML with maturation
- positive maturation: CD13, CD33, CD65, CD11b, CD15
- Acute myelomonocytic leukemia
- acute = 20% blasts
- myelo = has neutrophil lineage proliferation
- monocytic = 20% monocytic lineage
- monoblasts, promonocytes, monocytes
- coexpression CD64, CD15
- positive: NSE, CD14, CD4, CD11b, CD11c, CD64, CD36
- Acute monoblastic and monocytic leukemia
- 80% monocytic lineage
- minor neutrophil component
- monoblastic = monoblasts
- monocytic = mostly promonocytes
- Acute erythroid leukemia
- erythroleukemia (erythroid and myeloid)
- 50% erythroid, 20% of non-erythroids are myeloblasts
- erythroid: all stages, left shifted, dysplasia (megaloblastoid, multinucleated)
- myeloid: Auer rods, dysplasia (neutrophils, megakaryocytes)
- hypercellular marrow
- pure erythroid leukemia (erythroid only)
- 80% erythroids, few myeloblasts
- erythroblasts: MPO-, glycophorin+, hemoglobin+
- Ddx
- MDS: less than 20% blasts (including nonerythroids)
- AML with MDS: 20% blast with multilineage dysplasia in 50% of cells
- AML with increased erythroid
- erythroleukemia (erythroid and myeloid)
- Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
- 20% blast, of which 50% megakaryocytic
- megakaryoblasts: CD41+, CD61+
- marrow replaced by megakaryocytes and blasts
- Acute basophilic leukemia
- blasts and immature basophils
- Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
- panmyeloid proliferation with increased blasts
- myelofibrosis
- rule out AML with MDS
myeloid sarcoma
Down syndrome
blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm
Signout
- Acute myeloid leukemia (*** blasts by ***)
- Routine cytogenetic studies pending
- Myeloid mutation panel pending
