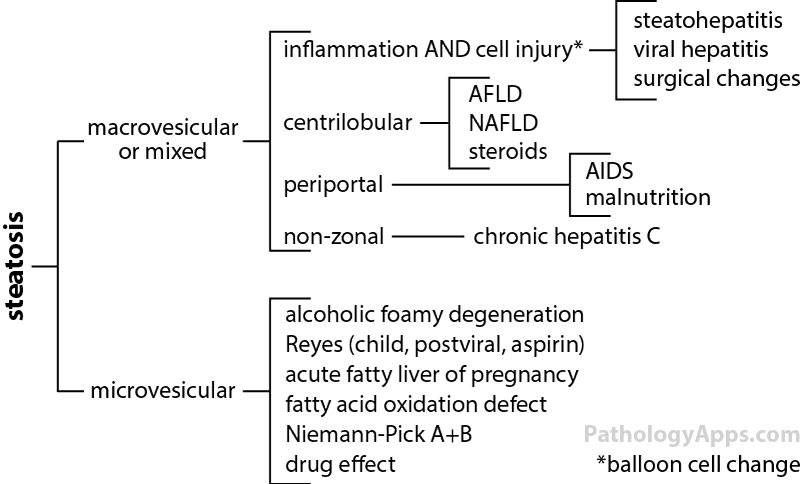
steatosis
Expand All | Collapse All
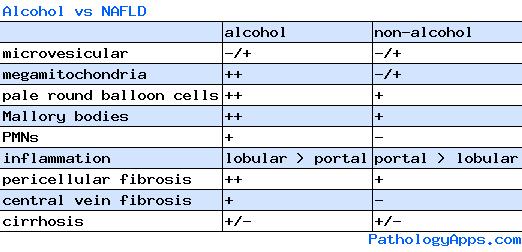
NAFLD = most common
- middle aged, but can be younger
- mild AST ALT elevation
- 20-30% can have low titer ANA, anti sm muscle
- association with metabolic syndrome (central obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, hyperglycemia/insulin resistance)
- neutrophils rare (vs AFLD)
Alcohol liver disease = striking cellular injury, PMNs
- central vein sclerosis
- striking balloon cells, mallory hyaline
- neutrophils in lobules
- diffuse pericellular fibrosis
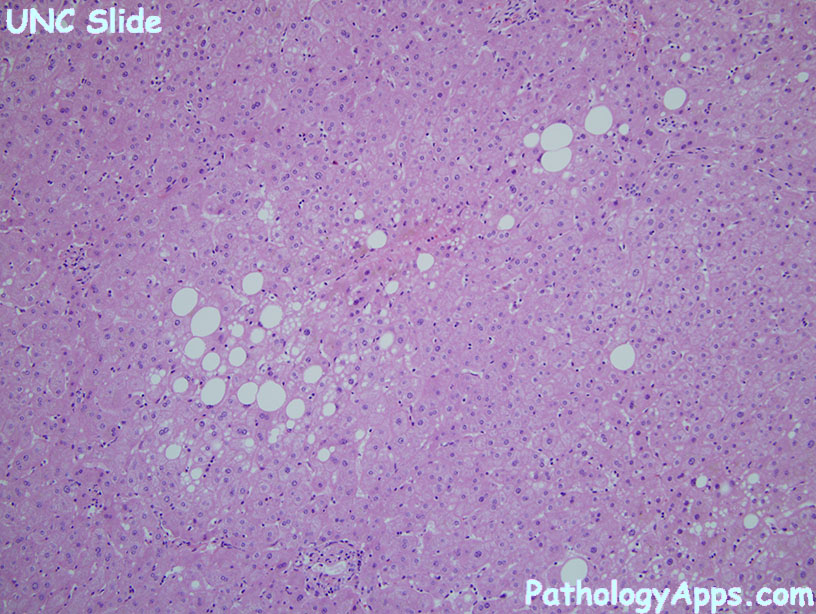
Steatosis = fat
- macrovesicular: EtOH, obesity, DM, HLD, steroids
- microvesicular: Alcoholic foamy liver degeneration, HAART, pregnancy, Reye syndrome, tetracycline, valproic acid, malnutrition, other metabolic/genetic conditions
- 10% of NAFLD can have small circumscribe patches of microvesicular steatosis
- no risk of fibrosis
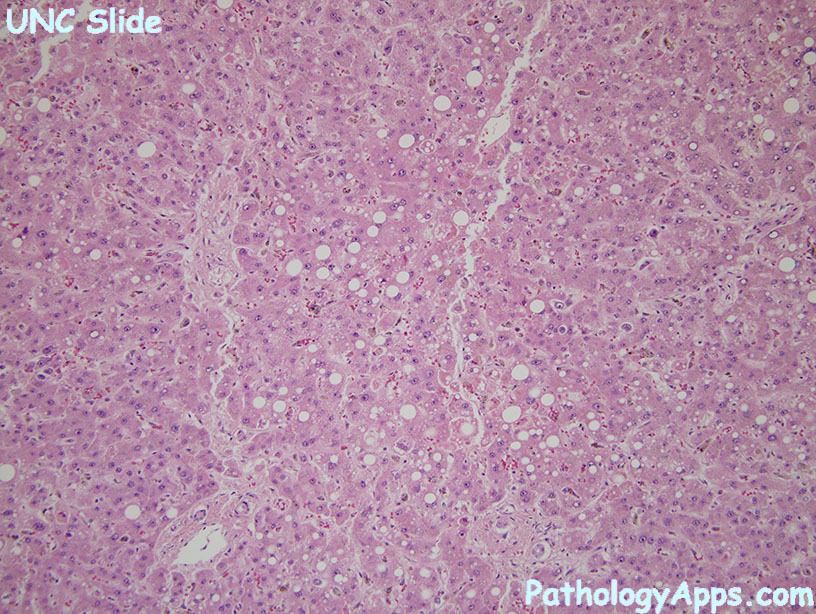
Steatohepatitis = fat + lobular inflammation + balloon cell
- ddx surgical hepatitis in wedge/resections
- ddx hepatitis C if too much inflammation
- 30% develop fibrosis, 15% cirrhosis
Other features
- lipogranuloma: histiocytic aggregates w lipid droplets
- megamitochondria: more common in steatohepatitis
- glycogenated nuclei in 45-65%, assoc diabetes
Fibrosis Staging
- 1a: mild pericellular on trichrome
- 1b: moderate pericellular on H&E
- 1c: portal fibrosis only
- 2: portal fibrosis and pericellular fibrosis
- 3: briding fibrosis
- 4: cirrhosis
NAFLD activity score
- fat
- 0: minimal < 5%
- 1: mild <= 33%
- 2: moderate <= 66%
- 3: marked 67+
- balloon cells
- 0: none
- 1: few
- 2: many
- lobular inflammation
- 0: none
- 1: 1 foci per 20x field
- 2: 2-4 foci per 20x field
- 3: 5+ foci per 20x field
