mouth

Expand All | Collapse All
Normal
- stratified squamous epithelium
- basement membrane
- lamina propria
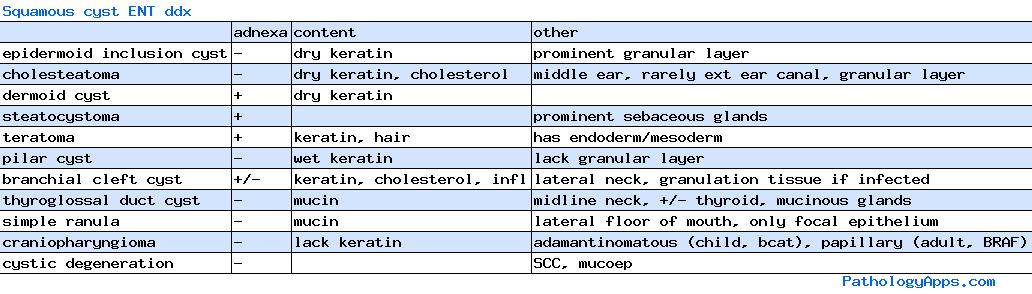
Non-neoplastic
- lichen planus
- mucous membrane pemphigoid
- pemphigus vulgaris
- hairy leukoplakia
- aphthous stomatitis
- traumatic ulcerative granuloma
- fordyce granules
- amalgam tattoo
- ectopic thyroid
- infections
- candidiasis
- HSV
- actinomycosis
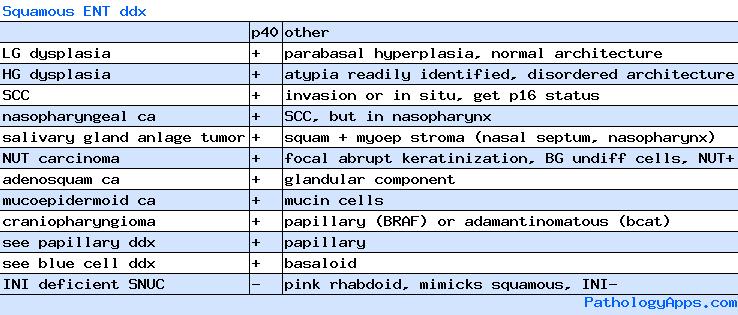
WHO neoplasms
- malignant epithelial
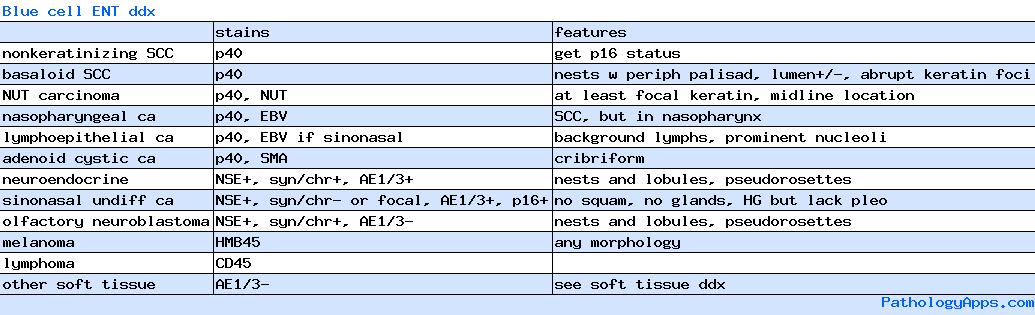
- SCC
- verrucous carcinoma
- basaloid SCC
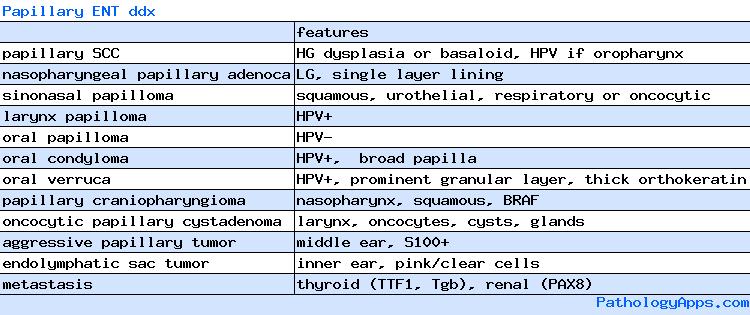
- papillary SCC
- spindle cell carcinoma
- acantholytic SCC
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- carcinoma cuniculatum
- lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- SCC
- epithelial precursor lesions
- squamous cell hyperplasia
- dysplasia
- mild
- moderate
- severe
- carcinoma in situ
- benign epithelial
- papillomas
- squamous papilloma
- condyloma acuminatum
- focal epithelial hyperplasia
- granular cell tumor
- keratoacanthoma
- papillomas
- salivary gland tumors
- see salivary gland section
- soft tissue
- Kaposi sarcoma
- lymphangioma
- ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor
- focal oral mucinosis
- congenital granular cell epulis
- fibroma
- lobular capillary hemangioma
- peripheral ossifying fibroma
- peripheral giant cell granuloma
- hematolymphoid
- lymphoma
- DLBCL
- MCL
- follicular lymphoma
- MZL
- Burkitt lymphoma
- T-cell lymphoma
- plasmacytoma
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- myeloid sarcoma
- follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
- lymphoma
- melanoma
- metastasis
TNM (useful for grossing)
- T
- T1: <= 2cm
- T2: 2-4cm
- T3: > 4cm
- T4a
- lip: involves cortical bone, inferior alveolar nerve, floor of mouth, or skin
- oral cavity: involves cortical bone, deep/extrinsic tongue muscle, maxillary sinus, skin
- oropharynx: involves larynx, deep/extrinsic tongue muscle, medial pterygoid, hard palate, mandible
- T4b
- lip and oral cavity: involves masticator space, pterygoid plate, skull base, or encases carotid artery
- oropharynx: involves lateral pterygoid muscle, pterygoid plates, lateral nasopharynx, skull base, or encases carotid artery
- notes
- bone involvement can't be just superficial erosion
- deep/extrinsic tongue muscles: genioglossus, hyoglossus, palatoglossus, styloglossus
- N (cervical nodes)
- N1: single ipsilateral node, <= 3cm
- N2a: single ipsilateral node, 3-6cm
- N2b: multiple ipsilateral nodes, <= 6cm
- N2c: contralateral or bilateral nodes, <= 6cm
- N3: > 6cm
Staging
- 0: Tis
- I: T1
- II: T2
- III: T3 or N1
- IVA: T4a or N2
- IVB: T4b or N3
- IVC: M1
