HCC
-[3-li043-4].jpeg)
Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- 85% due to chronic viral infection: HBV, HCV
- cirrhosis
- other etiologies: EtOH, iron overload, hereditary hemochromatosis, alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
- associations: elevated AFP
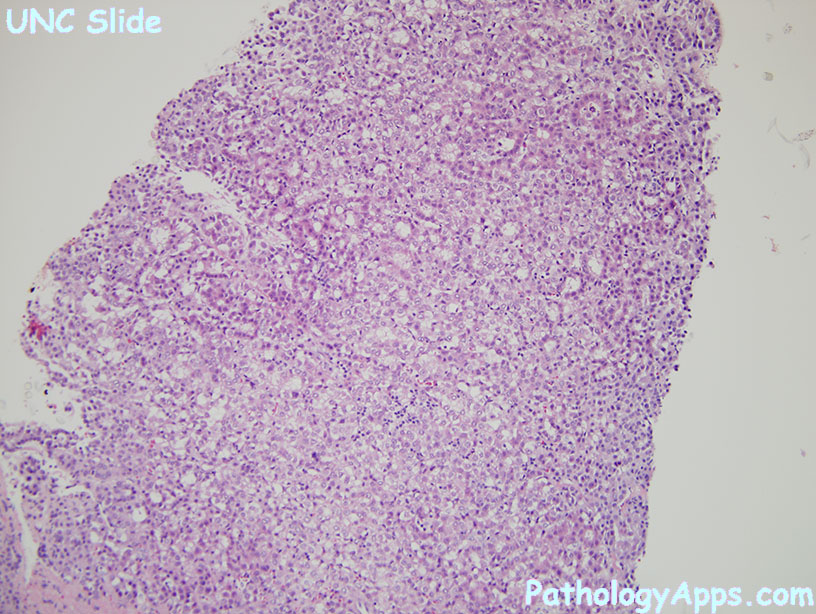
Histology
- architecture
- trabecular
- pseudoglandular
- compact/solid
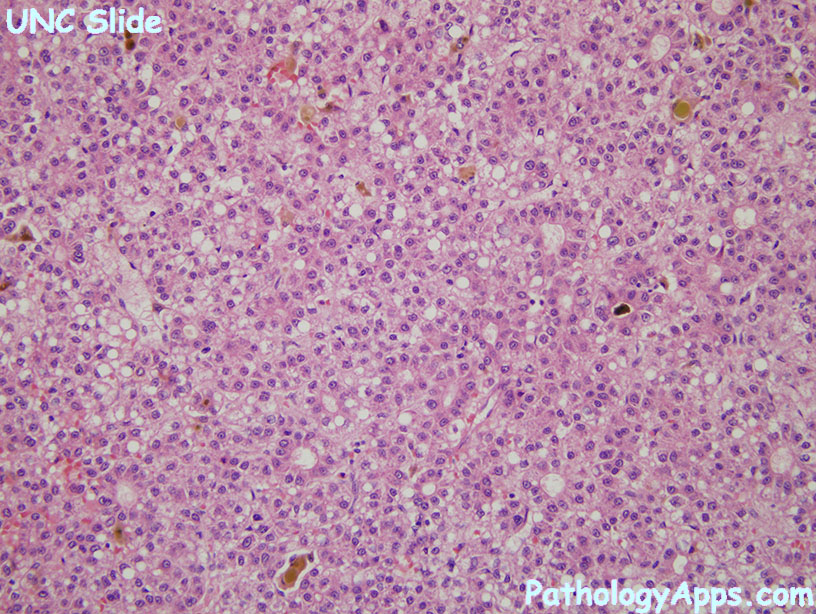
- cytology
- classic: resembles hepatocytes
- other variants: pleomorphic, clear cells, fatty change
- other features: bile plugs, hyaline bodies, pale bodies, ground glass inclusions
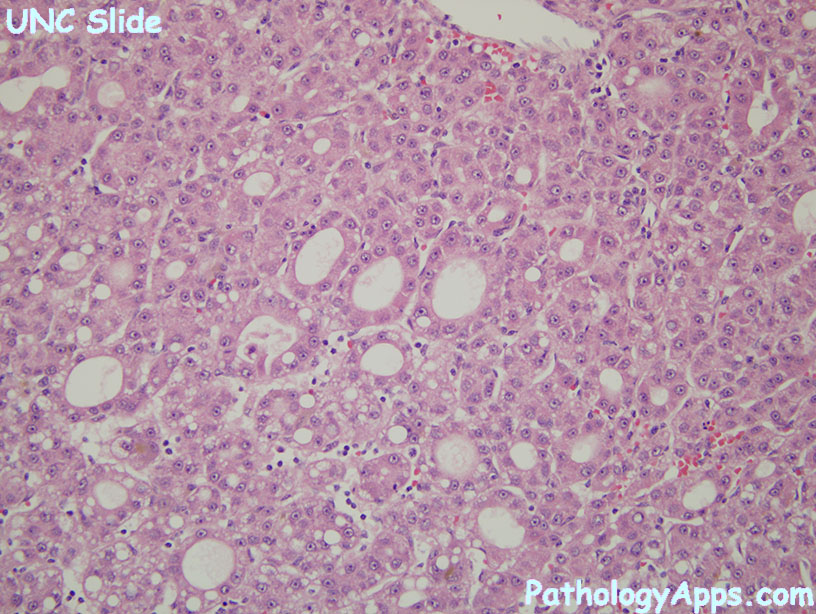
- other features
- plates > 2 cells thick
- pseudoglands: abnormal bile canaliculi between tumor cells, contains PAS+ pink fluid
- capillarization: sinusoid endothelial cells become CD34+
- neovascularization: unpaired arteries that are not part of portal triad
- lacks portal tracts (entrapped portals may be seen in periphery)
Subtypes
- fibrolamellar carcinoma
- scirrhous HCC
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- lymphoepithelioma like carcinoma
- sarcomatoid HCC
Stains
- HSP70 > 10%
- glypican 3
- glutamine synthetase > 10%
- positive: HepPar1 (90%), CD34 stains sinusoids, AFP, CK8, CK18
- negative: CK19, CK20, EMA
Grading
- well-differentated: resembles normal hepatocytes with pseudoglands and fatty change, usually size < 2cm
- moderately differentiated: plates > 2 cell thick, prominent nucleoli, usually size > 3cm
- poorly differentiated: solid tumor nests, lack sinusoid, marked atypia/pleomorphism, large size
- undifferentiated: solid, little cytoplasm, round or spindle cells
