DCIS


Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- 20-25% of breast cancers
- most detected by imaging (calcifications), but can be a palpable mass
- DCIS is associated with undetected or future invasive cancer
- prognosis
- size, nuclear grade, comedo necrosis, margin status
- hormone: ER+ treated with tamoxifen. PR controversial.
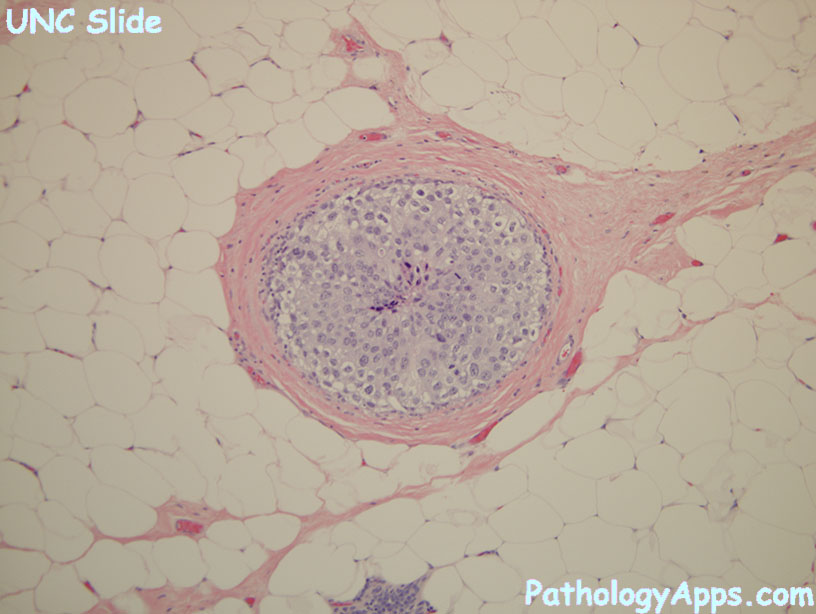
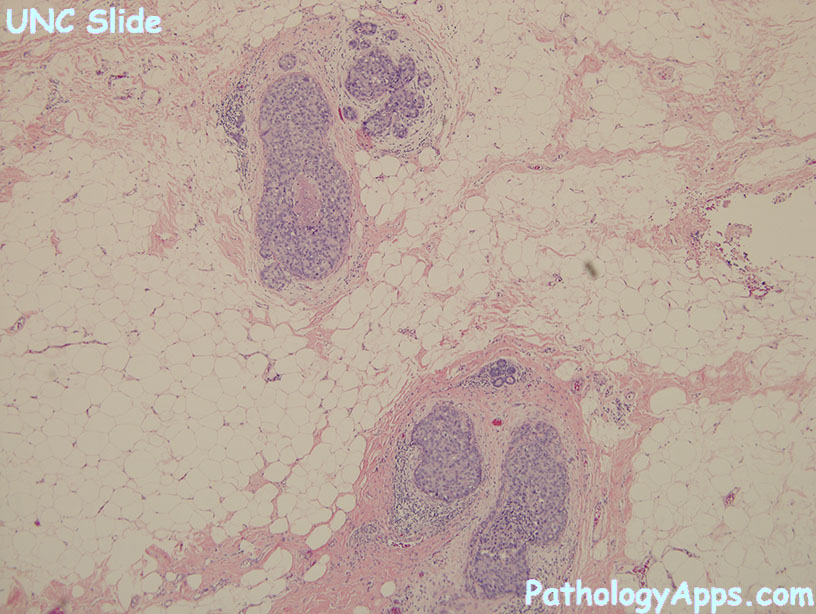
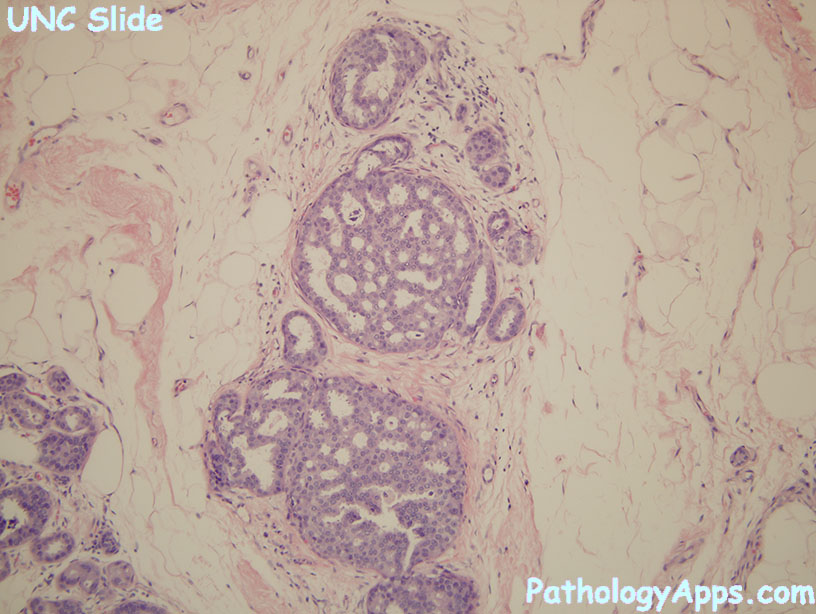
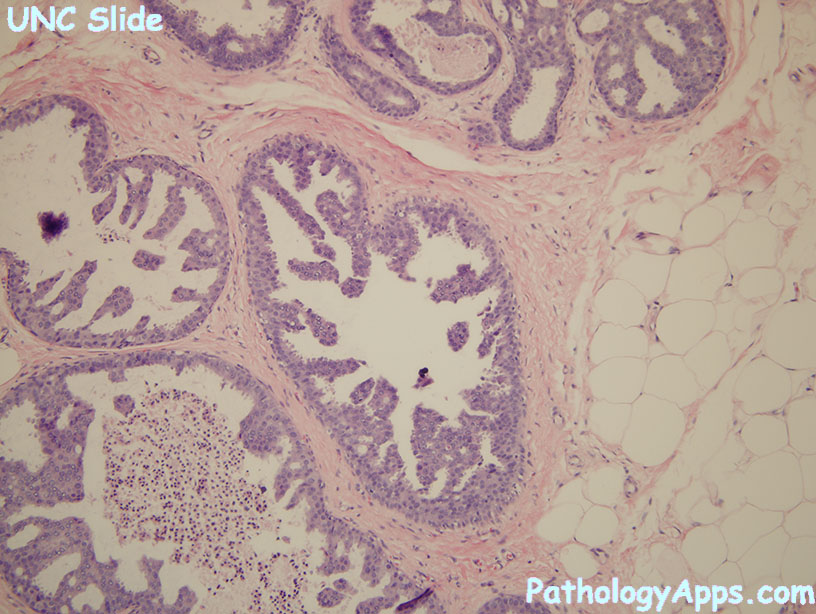
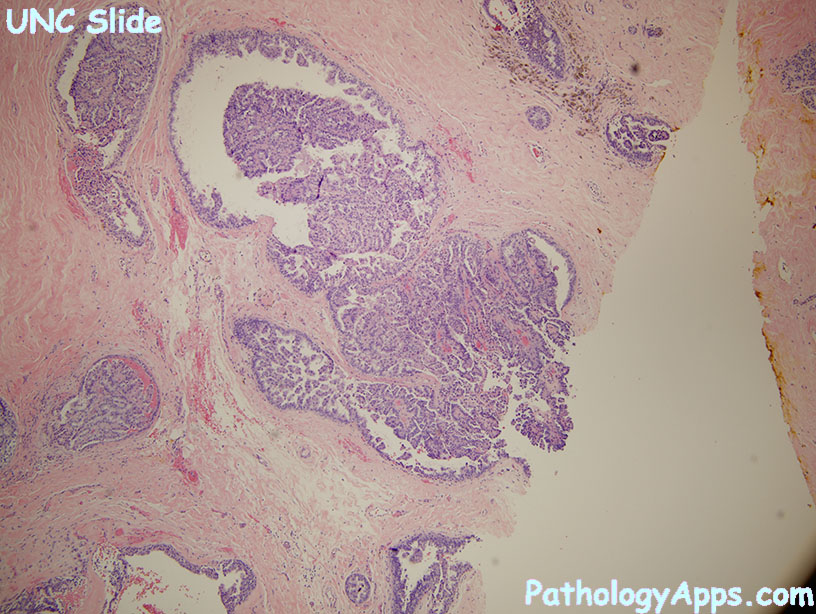
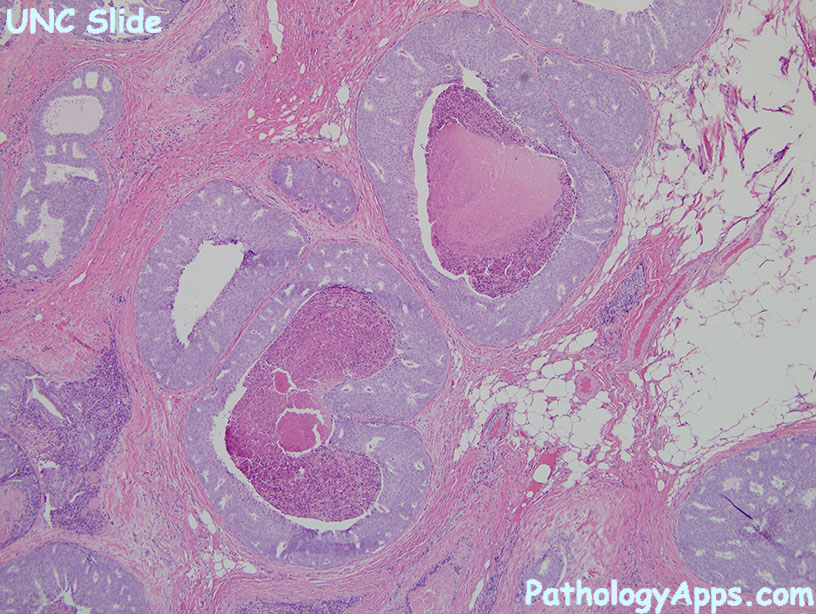
Histology
- nuclear grades
- low
- small monomorphic cells, even distribution (non-overlapping), good luminal polarization
- rare mitosis, inconspicuous nucleoli, even chromatin, uncommon necrosis
- patterns: bridge archs, micropapillary, cribriform, solid
- intermediate
- mild to moderate cell variability
- can have mitosis, necrosis, coarse chromatin, variable nucleoli
- high grade
- overt pleomorphism
- common mitosis, prominent nucleoli, clumpy chromatin, comedo necrosis
- patterns: solid, cribriform, micropapillary
- low
- traditional subtypes
- solid
- cribriform
- papillary
- micropapillary
- comedo type necrosis: comedo necrosis, but low grade
- comedo DCIS: high grade with comedo necrosis
- microinvasion: 1 mm extension through myoepithelial layer
Stains
- myoepithelial markers+ (vs loss in invasive carcinoma)
- smooth muscle myosin
- p63
- CK5/6 negative (vs UDH positive)
- E-cadherin+ (vs lobular negative)
- ER (75-80%), PR (lower), positive is >= 1% of cells
- HER2 not as useful because it's frequently overexpressed in DCIS
Grading
- low grade: monomorphic uniform cells
- intermediate grade: in between
- high grade: ugly cells
Ddx
- UDH with necrosis
- ADH
- florid or pleomorphic LCIS
Sign out
- DCIS, ___ grade, ___ pattern
- on excisions: size, margin
- no invasive carcinoma
- microinvasion on bx requires sentinel lymph node
- give ER/PR status
