Crohn disease
Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- female > male
- age: peaks at 20-30, 60-70
- chronic, relapsing diarrhea
- associations: familial
- labs: ASCA+, pANCA-
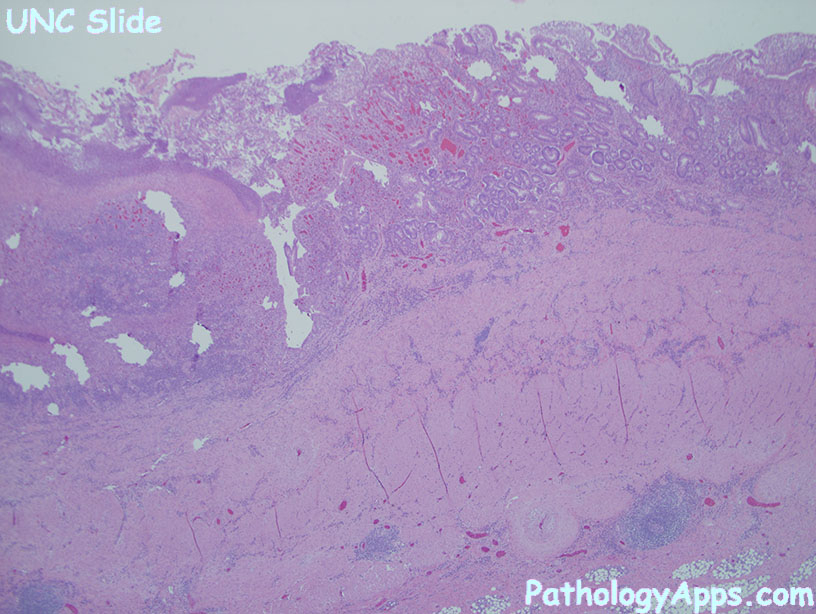
Gross
- erosions, serpigenous ulcers, cobblestoning
- skip-lesions
- strictures, fissures, fistulas
- can be anywhere in GI tract
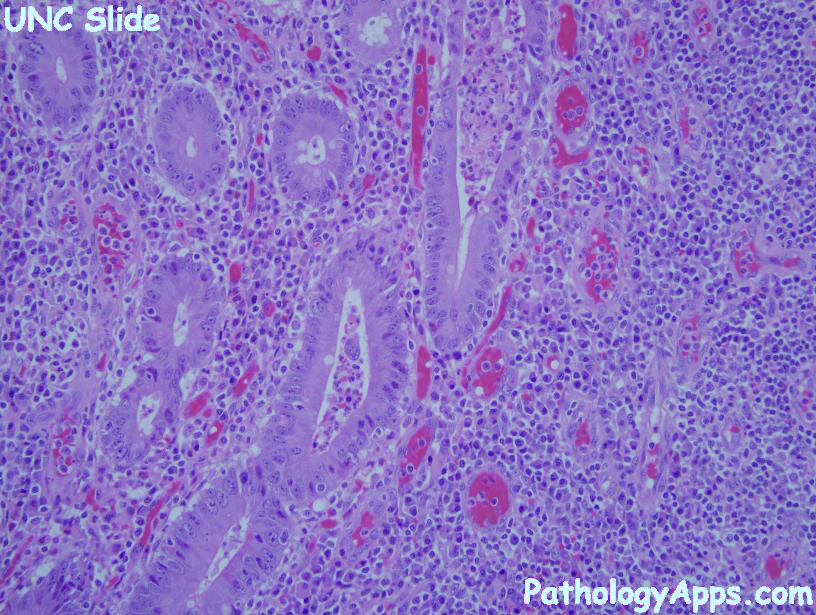
Histology
- IBD features
- erosions, ulcerations
- crypts: crypt dropout, cryptitis, crypt abscess
- fibrosis
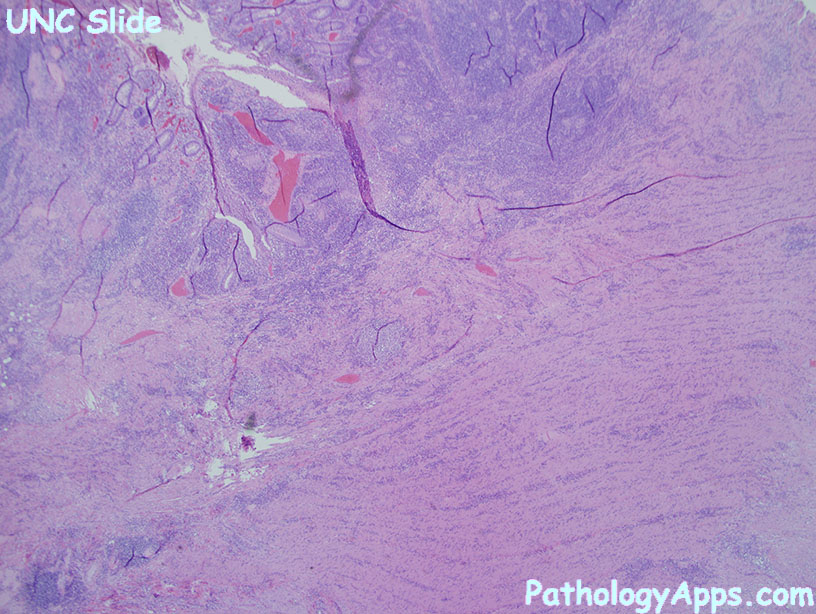
- Crohn features: chronic inflammation, transmural, poorly-formed granuloma, fistulas
Ddx
- infectious colitis
- PMN predominance
- drug induced colitis
- ulcerative colitis
- peptic ulcer
Signout
- biopsy
- moderate/severe chronic active colitis/enteritis
- no dysplasia or viral cytopathic effect identified
- Comment: these findings could be consistent with Crohn's disease in the appropriate clinical setting
- resection
- moderate/severe chronic active colitis/enteritis
- transmural lymphoid aggregates with occasional poorly formed granuloma
- ___ other IBD and Crohn specific features
- consistent with history of Crohn disease
- surgical margins viable and uninvolved
- no dysplasia or viral cytopathic effect identified
