urothelial carcinoma

Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- risk factors: smoking, aniline dyes, arsenic
Types
- invasive: lamina propria invasion
- non invasive: no invasion, confined to urothelium
- male > female (3:1)
- mean age 69
- site: posterior or lateral walls close to ureter orifice (70%)
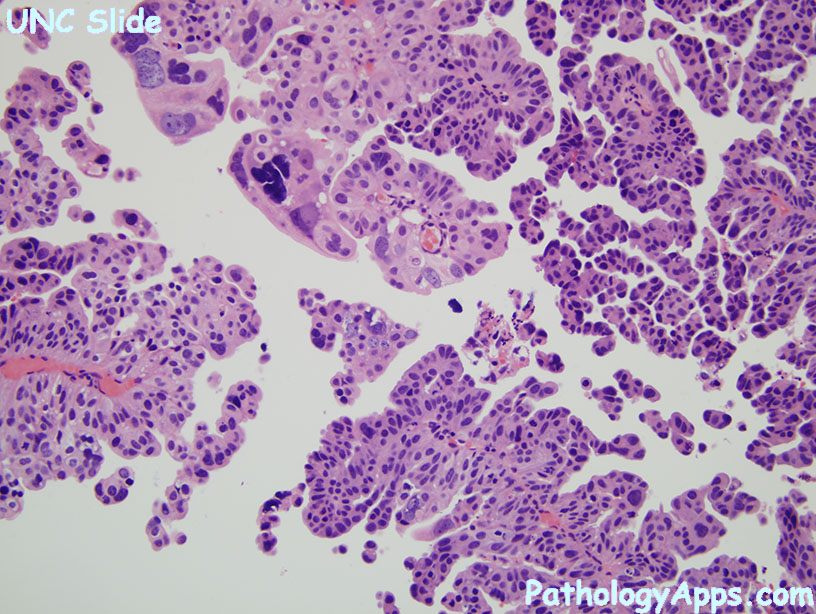
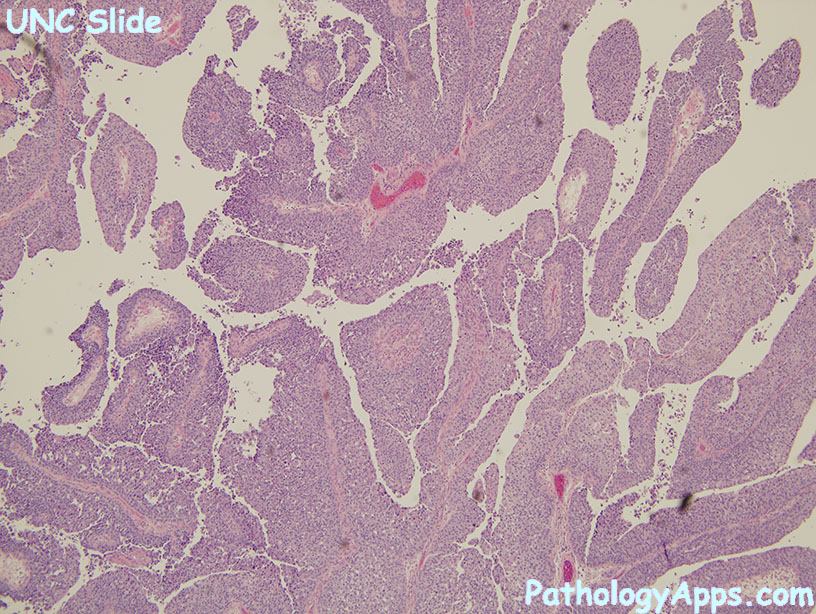
- papillary: usually T1 tumors
- non papillary: usually T2+ tumors, high grade
- low grade (occasional mitosis)
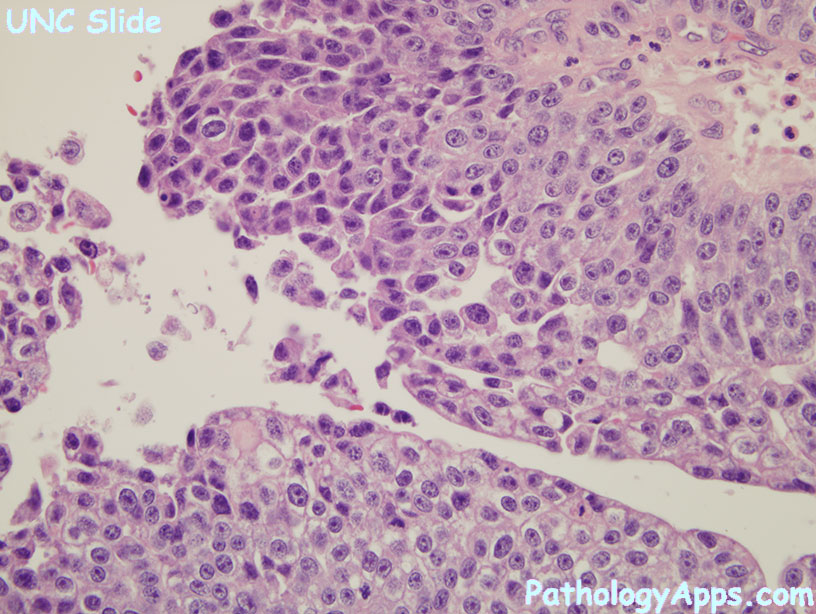
- high grade features
- frequent mitosis, esp high up in epithelium
- fusion of papillary stalks
- architecture distortion
- cytologic atypia, pleomorphism
- lack polarity, maturation
Histology
- architecture: papillae can be fused, branched, or lost all together
- polarity loss: focal to complete
- mitosis not confined to basal layer
- nuclear enlargement with variation in size and shape
- chromatin is more clumpy
Invasion
- irregular nests
- basement membrane disruption
- tentacle projections
- single cells
- +/- stromal response: desmoplasia, inflammation
- pitfalls: Brunn nests, muscularis mucosae, lamina propria fat, microcystic variant (invasive), nested variant (invasive)
Variants
- with squamous differentiation (21%, most common)
- give percentage of squamous component
- can have basaloid or clear cell features
- stains: CK14+
- UC with glandular differentiation
- 6%
- true glands: don't count cytoplasmic mucin without glandular structure or necrosis pseudoglands
- structures: tubules, enteric glands with mucin, colloid mucinous (nests of cells floating in mucin)
- give percentage of glandular component
- stains: MUC5
- with trophoblastic differentiation: syncytiotrophoblasts
- nested (rare, aggressive, but benign looking)
- architecture looks like benign von Brunn nests
- but contains foci of anaplastic cells
- microcystic
- micropapillary
- muscularis invasion (needs biopsy with muscularis)
- stains: EMA, CK7, CK20
- lymphoepithelioma-like
- epithelial: undifferentiated, pleomorphic, CK+
- lymphoid stroma
- lymphoma-like and plasmacytoid: looks hematopoietic, but CK+ and lymphoid negative
- sarcomatoid +/- heterologous elements
- giant cell
- clear cell
- lipid cell: cells distended with fat, mimicks signet ring cells
- undifferentiated
Stains
- positive: CK7 (100%), CK20(67%), p63 (81-92%), GATA3 (67-90%)
- uroplakin most specific, but not sensitive
- high grade can lose CK7 and 20
- if uncertain muscularis propria invasion, order SMA
