transplant rejection
Expand All | Collapse All
Histology
- acute rejection
- perivascular, interstitial
- mononuclear infiltrates
- can have endothelialitis and lymphocytic bronchiolitis
- chronic rejection
- fibrosis, scarring of airways and vessels
Stains
- trichrome for fibrosis
Adequacy
- 5 pieces at least
- well-expanded alveolated lung tissue
- 3 levels at least
Grading
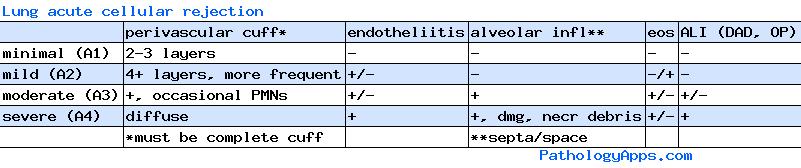
- A: acute cellular rejection
- 0 = none = no mononuclear infiltrate, hemorrhage or necrosis
- 1 = minimal = scattered perivascular infiltrate (cuffing)
- incomplete cuffing unlikely to be rejection
- 2-3 cell thick, lymphoplasmacytic
- no eosinophils or endothelialitis
- 2 = mild = more perivascular infiltrates, eosinophils, endothelialitis, airway inflammation
- 3 = moderate = extension of infiltrate to alveolar septa and airspaces
- 4 = severe = prominent alveolar pneumocyte damage and endothelialitis, intraalveolar necrotic debris
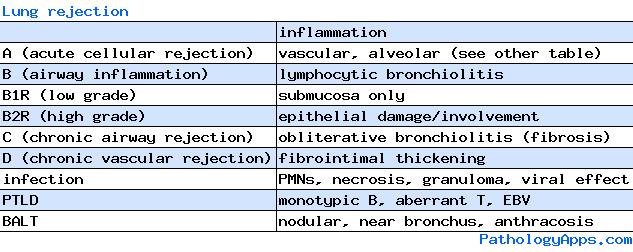
- B: airway inflammation: lymphocytic bronchiolitis
- 0 = none = no evidence of bronchiolar inflammation
- 1R = low grade = mononuclear cells in submucosa
- 2R = high grade = epithelial damage (necrosis, metaplasia, intraepithelial lymphocytes), eosinophils, plasmacytoid cells
- X = ungradable
- C: chronic airway rejection - obliterative bronchiolitis
- 0 = absent
- 1 = present
- D: chronic vascular rejection - fibrointimal thickening of vessels
- only in wedge resections
- AMR: controversial, no consensus
- I: latent humoral response = circulating antibodies only
- II: silent humoral response = C4d deposition
- III: sub-clinical humoral rejection = tissue pathology
- IV: humoral rejection = graft dysfunction
