inverted urothelial papilloma
Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- age: peaks 60-70s
- male > female (4:1)
- location: bladder (70%, trigone most common), ureter, renal pelvis, urethra
Histology
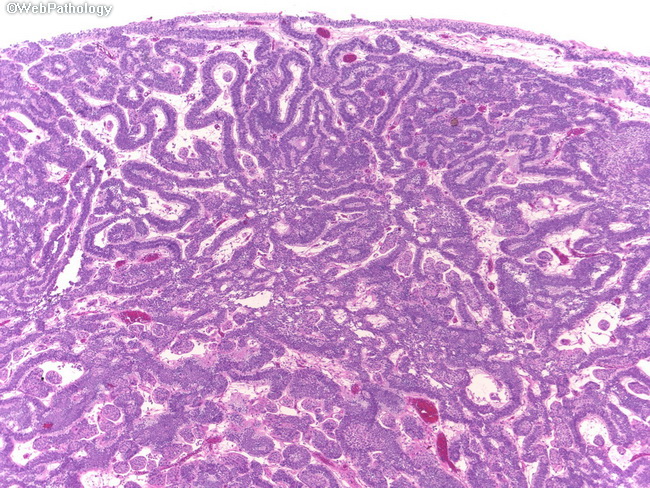
- inverted papillary architecture: urothelial cells facing central fibrovascular core, basal cells face outward
- benign cytology: lack mitosis, lack nucleoli, fine chromatin, uniform nucleus
- focal squamous metaplasia, nonkeratinizing
- subtypes
- trabecular: interanastomosing sheets, cystic areas
- glandular
