adenoma
Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- associations: FAP
- small intestine adenoma usually periampulla
- higher risk if: 3+ adenoma, HG dysplasia, villous features or over 1 cm size
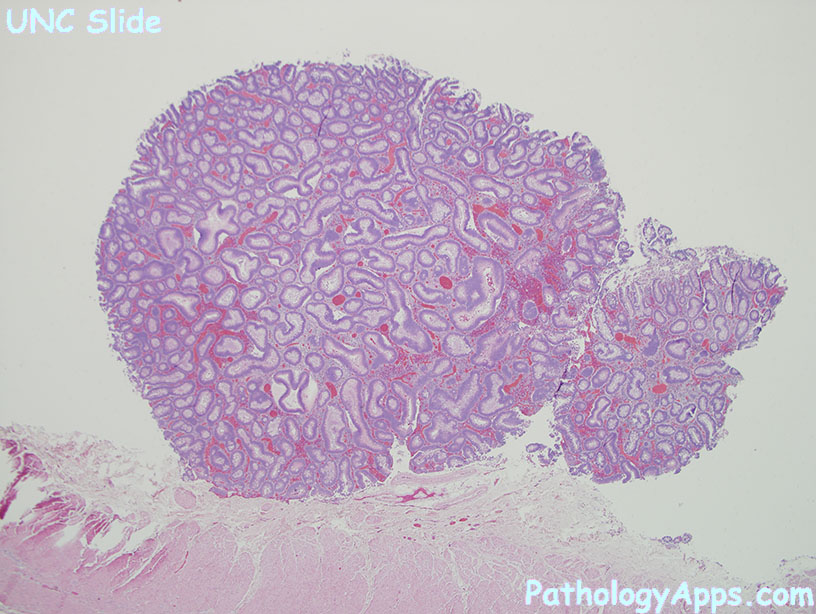
Gross
- can be elevated, flat or depressed
- can be stalked or sessile
- non-elevated lesions are recognized by erythema
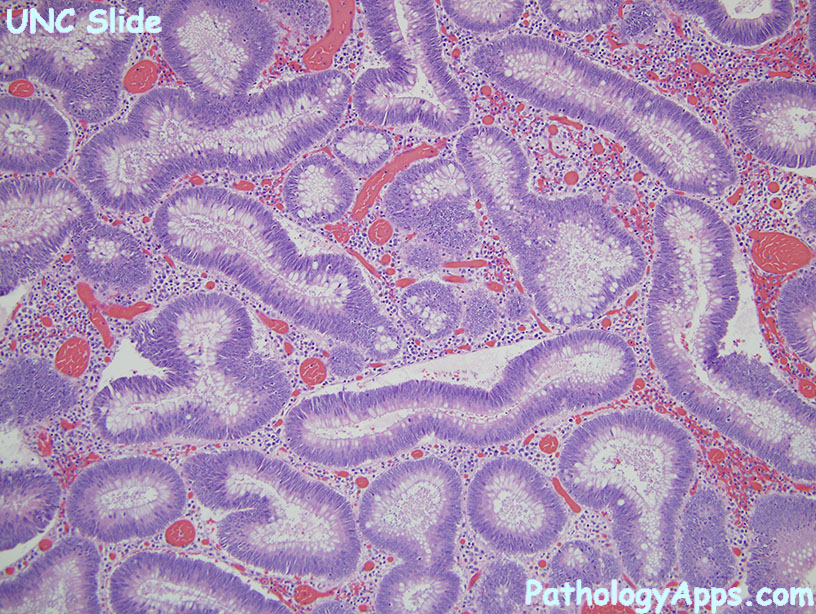
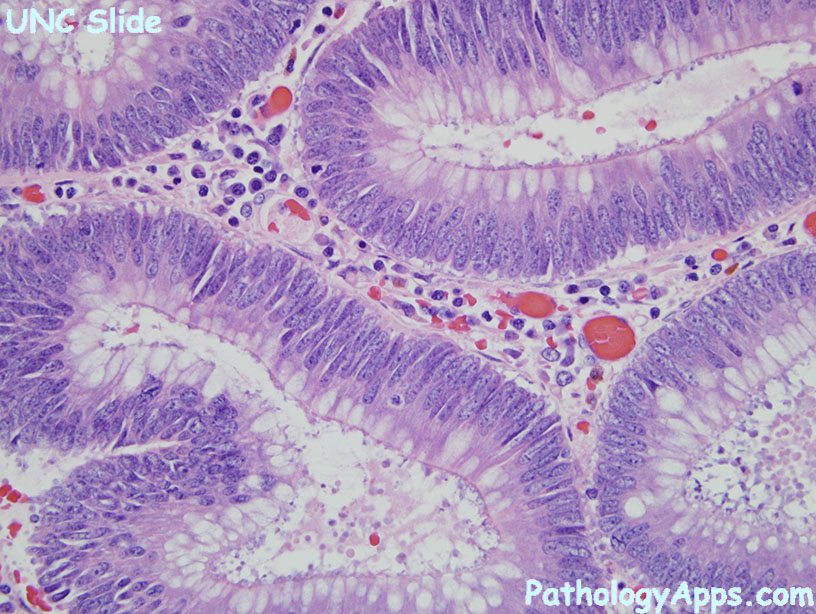
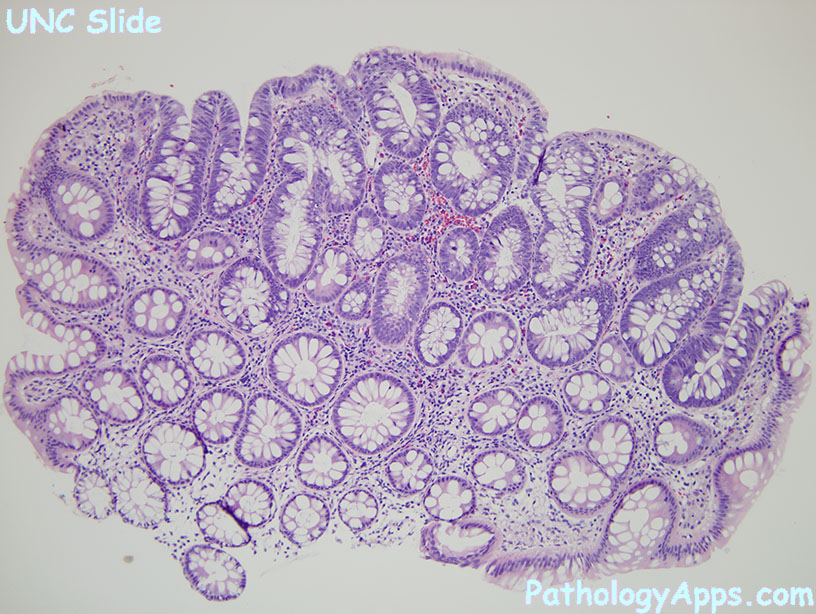
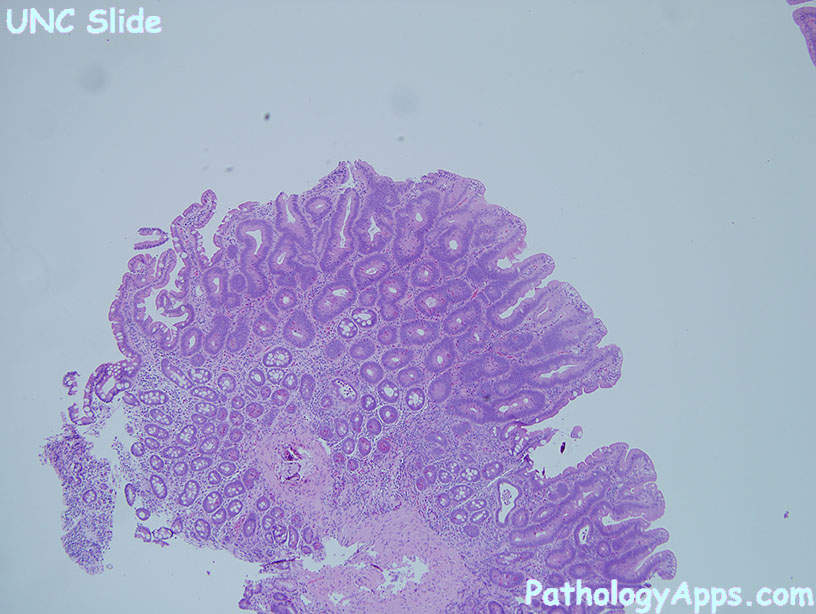
Histology
- hypercellular
- nuclear atypia: enlarged, hyperchromatic, stratification, polarity loss
- dysplastic glands in at least 80% of luminal surface
- HG dysplasia if: severe atypia in the context of cribriform, polarity loss, or stratification
- pseudoinvasion = prolapse of neoplastic glands into submucosa (have rounded contours)
- sporadic = lots of apoptosis
- Lynch syndrome = intraepithelial lymphs
- look for invasion: angulated glands, single cells, desmoplasia
Types
- tubular adenoma
- villous adenoma
- tubulovillous adenoma
- serrated adenoma
- mixed hyperplastic polyp/adenoma
- villomicroglandular adenoma
