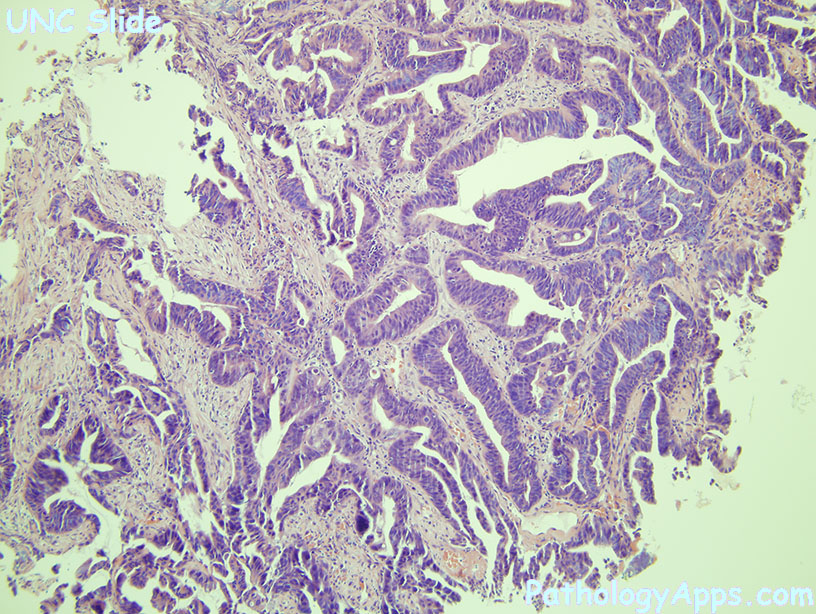
adenocarcinoma

Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- average age 70s
- associations: family history, IBD, HNPCC
- tx: resection is most effective for T1 and T2 stage. Chemo for advanced stage.
- FAP: autosomal dominant, colon filled with polyps, APC gene, wnt pathway, tx prophylactic colectomy
- Gardner syndrome: FAP with extracolonic features (osteomas, epidermal cysts, fibromas)
- HNPCC: MMR/MSI, colorectal, gyn (endometrial, ovarian) and gastric cancer. Colonoscopy starting age 20 or 10 years younger than family hx
- Turcot syndrome: CNS tumor + hereditary colonic cancer syndrome
Gross
- fungating, ulcerated, or polypoid
Histology
- architecture: irregular, complex crypts, cribriforming
- pink necrotic debris in lumens
- high grade dysplasia (round nuclei, hyperchromasia, stratification)
- desmoplasia
- suspect HNPCC if: lots of lymphocytes, proximal mucinous or poorly differentiated carcinoma
Types
- cribriform comedo type adenocarcinoma
- medullary carcinoma
- micropapillary carcinoma
- mucinous adenocarcinoma
- serrated adenocarcinoma
- signet ring carcinoma
Grading
- well, moderately, poorly, and undifferentiated
- based on % gland formation
Stains
- positive: CK, CK20 (variable in MSI high), CEA
Molecular
- sporadic: APC, KRAS, p53, 18q21 LOH (SMAD2, 4)
- hereditary: HNPCC = mismatch repair (MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, PMS2) -> microsatellite instability
Signout
- bx: superficial fragments of invasive moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma
