Wilms tumor

Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- mean age: 3-4 years
- malignant, most common pediatric renal malignancy
- syndromes
- WAGR: Wilms, aniridia, genitourinary malformation, mental retardation, WT1 (11p13) deletion
- Denys-Drash syndrome: mesangial sclerosis, pseudohermaphroditism, Wilms, WT1 point mutation
- Beckwith-Wiederman syndrome: hemihypertrophy, macroglossia, omphalocele, visceromegaly, WT2 (11p15)
- hemihypertrophy
- familial nephroblastoma
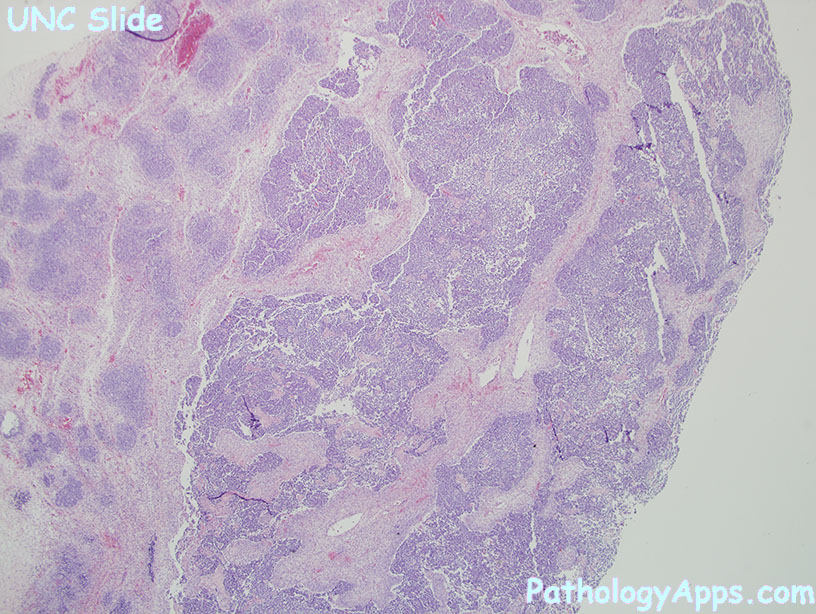
Histology
- border: pushing border
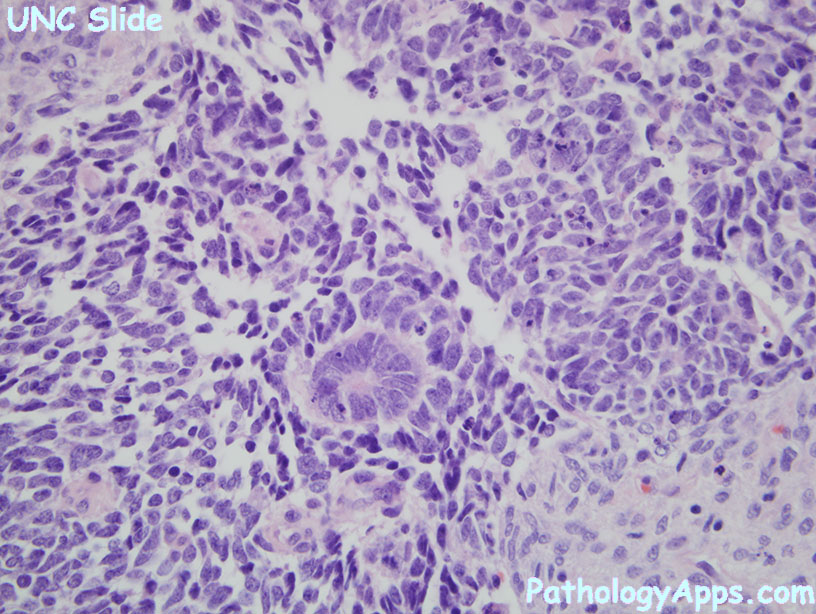
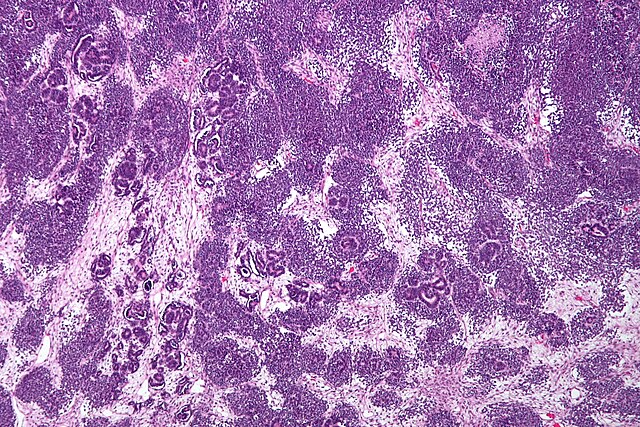
- triphasic (may also be biphasic or monophasic)
- blastemal cells: small round blue cells
- epithelial: recapitulates nephrogenesis, tubules, papillary, primitive rosette-like structures. Can have heterologous mucinous or squamous epithelium.
- stroma: skeletal muscle, fibroblasts, fat, cartilage, bone, ganglion, glia
- patterns
- diffuse blastemal: blastemal cells lack cohesiveness, invades adjacent connective tissue and vessels
- nodular and sperpentine blastemal: nests and cords of blastemal cells in fibromyxoid stroma
- diffuse anaplasia: ugly nuclei (more common in age > 5), abnormal mitotic figures.
- focal anaplasia criteria
- anaplasia is circumscribed
- anaplasia is confined to renal parenchyma
- anaplasia not in vascular spaces
- the rest of the tumor lacks severe nuclear atypia
- post-chemo changes
- necrosis
- xanthomatous histiocytic foci
- hemosiderin
- fibrosis
- maturation of components (eg. striated muscle)
Stains
- WT1 in immature elements, not sensitive or specific
Risk classification
- low risk
- cystic partially differentiated
- completely necrotic (post-chemo)
- intermediate risk
- non-anaplastic types
- only focal anaplasia
- high risk
- diffuse anaplasia
- blastemal type (post-chemo)
Staging
- I: completely resected (tumor within kidney)
- II: completely resected (tumor infiltrating capsule, sinus vessels, beyond kidney)
- III: residual tumor/positive margin
- SIOP also counts necrotic nodes as stage III
- IV: metastasis or positive lymph node
- V: bilateral involvement at diagnosis. Sub-stage each side separately.
