CML
Expand All | Collapse All
Clinical
- elderly
- leukocytosis, basophilia
- blast phase can involve nodes and soft tissue
Therapy & monitoring
- tx: HCT (curative), TKIs, cytotoxic agents (palliative)
- HCT: for young pts with suitable donor, those resistant to TKIs or with blast phase
- TKIs: for most pts
- cytotoxic agents: hydroxyurea, interferon alpha +/- cytarabine, busulfan
- monitoring: cytogenetics of marrow biopsies, PCR on peripheral blood
- response
- hematologic response
- WBC < 10k
- lack immature granulocytes
- < 5% basophils
- plt < 450
- spleen not palpable
- cytogenetic response
- complete response = no Ph chr detected by metaphase banding analysis of 20+ cells
- alternatively: < 1% BCR-ABL1 by FISH of at least 200 cells
- other: no response (> 95% Ph chr), minimal (66-95%), minor (36-65%), major (1-35%)
- molecular response
- international scale = ratio of BCR-ABL1 to control (ABL1), on log scale
- MR2: 2 log reduction (1%), corresponds to complete cytogenetic response
- MR3: 3 log reduction (0.1%), aka major molecular response
- MR4: 4 log reduction (0.01%)
- MR4.5: 0.0032%, not detectable in 32,000 control transcripts
- hematologic response
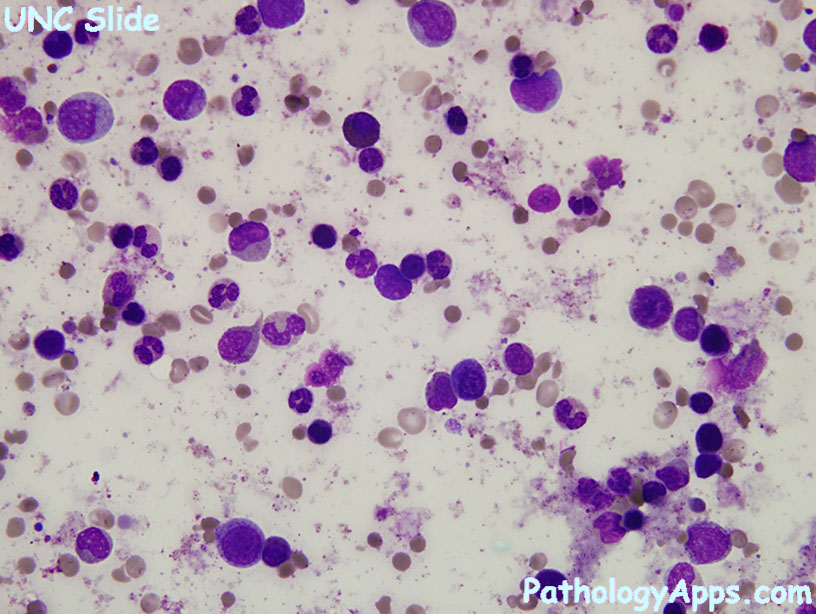
- residual disease clues
- hypercellularity
- clusters of dwarf megakaryocytes, gaucher like histiocytes
- basophilia
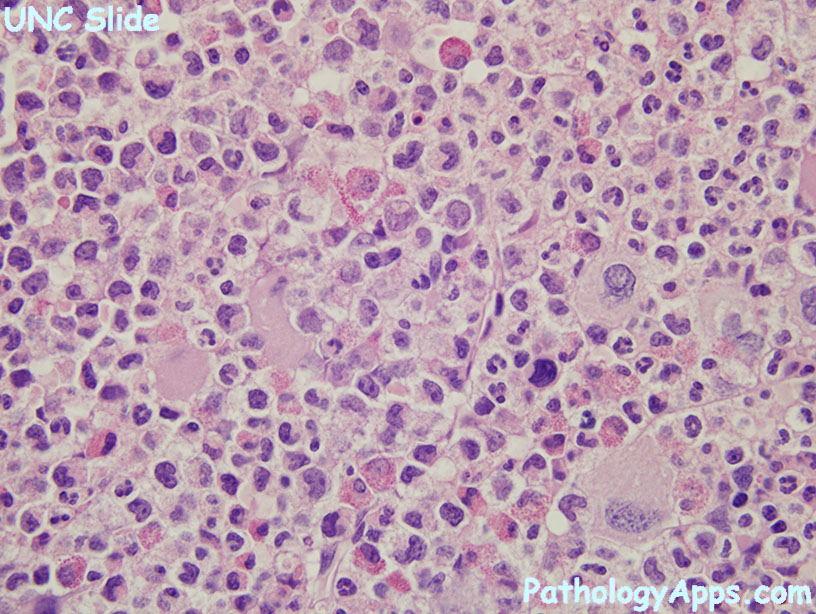
Phases
- chronic: < 2% blasts
- accelerated: 10-19% blasts
- blast: > 20% blasts
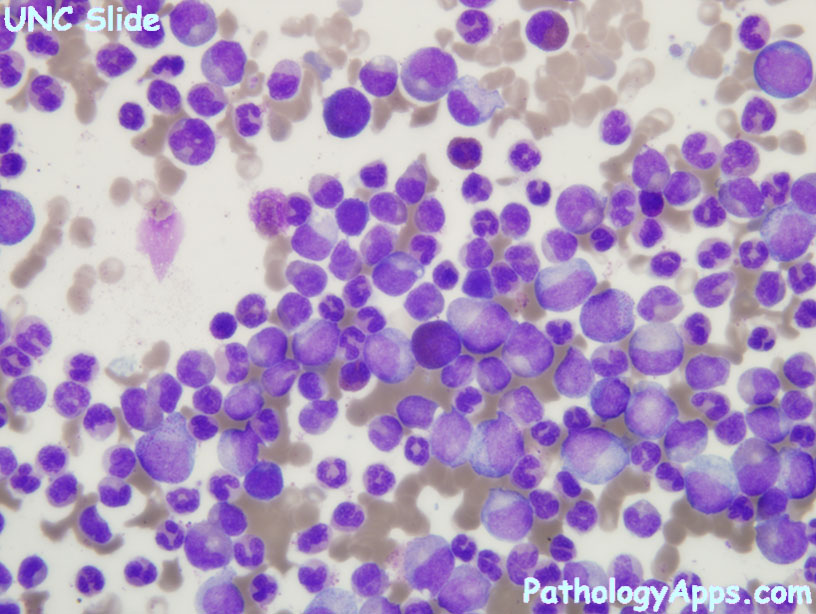
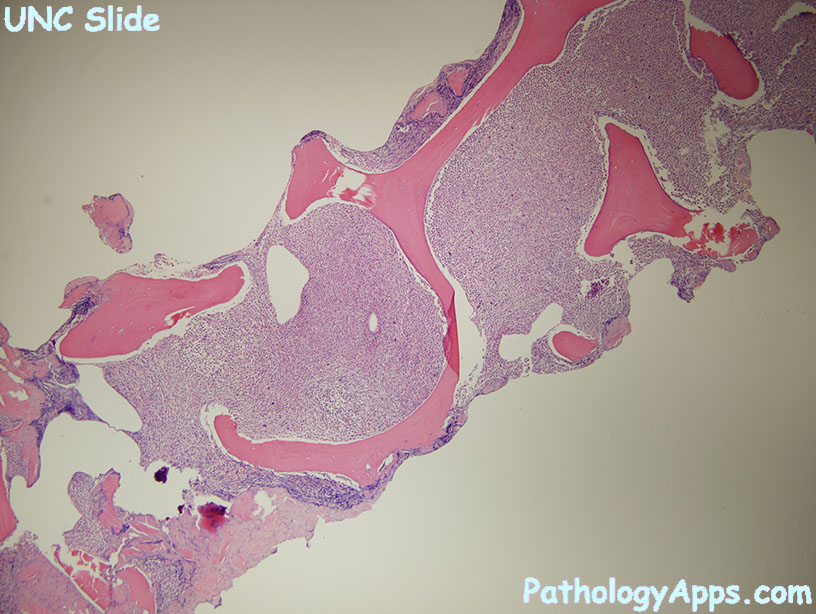
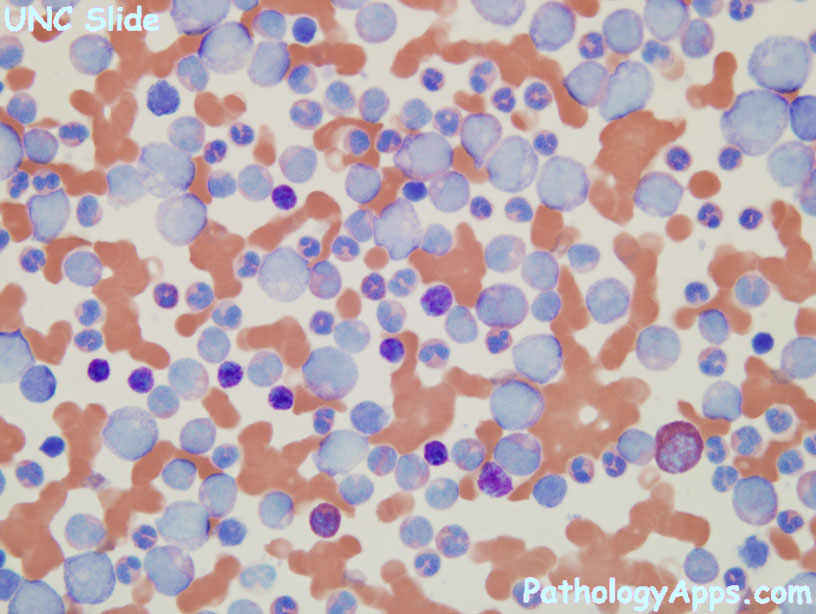
Morphology
- neutrophils of varying stages of maturation
- small hypolobated megakaryocytes
- pseudo-gaucher cells, sea blue histiocytes
Molecular
- BCR-ABL1, t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) (> 90% of cases)
- BCR on chr 22, breaks apart at MBCR region (exon 12-16)
- ABL on chr 9
- p210 is resulting fusion protein that has increased tyrosine kinase activity
- alternative: BCR breaks at mBCR (exon 1-2) -> p190 -> Ph+ ALL, CML with increased monocytes (CMML-like)
- alternative: BCR breaks at uBCR (exon 17-20) -> p230 -> can have prominent neutrophil maturation, thrombocytosis
- cryptic translocations: detectable by FISH, but not karyotype
